Why 3D Printing is getting the wind in the sails?
Three-dimensional (3D) printing or additive manufacturing (AM) is popular for aiding innovations in many sectors, such as manufacturing, art, engineering, education, physics and lately, medicine. Mass customization ability and personalized design without additional cost, feasibility of materializing highly complex designs, low time and low labor-intensive process, inexpensive manufacturing, sustainable mechanism, and less carbon footprints are some of the features that intrigue manufacturers to switch over to 3D-printing. Research and development along the years has enabled researchers to carry out 3D printing of biocompatible complex materials, cells & cell lines, and functional living tissues by using supporting components.
3D Bioprinting Technology – does a printer really exist?
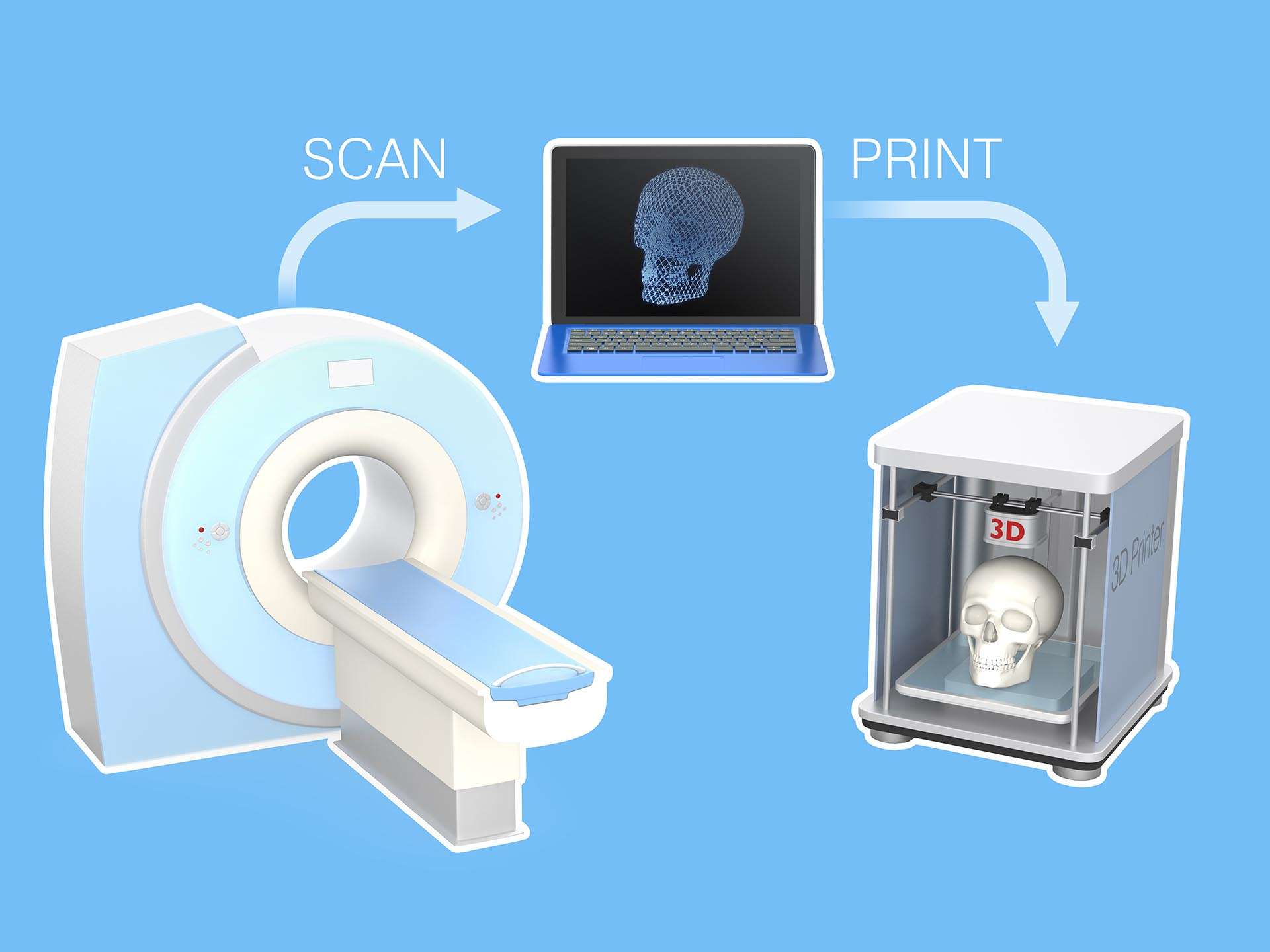
The 3D bioprinter is a reality. The method actually mimics the natural process of bio-development by embryonic cellular fusion. Scanned images of the target tissue/organ (that needs to be bioprinted) are obtained from computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonic scanning of the same. The image is processed graphically into a 3-dimensional detailed design of that target tissue/organ, and simultaneously the bioprinter machines are fed with bio-inks which are combinations of cells, cell aggregates, peptides, growth factors, etc. A matrix (like a bio-paper) is placed under the print syringes. The bio-ink is then dispensed from the bio-printer onto the gel matrix in a layer-by-layer mechanism, to generate the multi-cellular tissues at nano- to macro-scale as per the required output. Bio-printing techniques & modalities are multiple.
What is 3D Bio-printing getting at for the mass?
The revolutionary technology definitely comes at a price of various operational challenges including the choice of materials, types of cell, cellular growth and tissue-level differentiation factors, sensitivities of living cells to foreign objects, and construction of tissues as per the complex designs & patterns. However, multidisciplinary collaboration of technology has made it possible to use 3D bioprinting to attain variety of heights in the world of biotechnology, like generation and transplantation of plenty of tissue types such as bone, multilayered skin, vascular grafts, heart valves & septa, tracheal splints, and defined cartilaginous structures like ear and joint cartilages, etc. Apart from tissue structure development, many other applications viz. developing high-throughput 3D bioprinted tissue models for lab-level research, drug discovery and toxicology studies have also been abundant. Healthcare markets are hailed by 3D bioprinted dental applications, prosthetic limbs, and hearing devices which are available for use.
The Next-Gen 3D Bioprinting:
The ongoing researches and the promising future in this technology show that the next step in 3D bioprinting is going to be elimination of the organ transplantation crisis in medical care. The existing challenges and shortcomings on the way of developing fully functional living human organs are being addressed tactically with the help of developmental biology basics and technological progress like “computer-aided, jet-based 3D tissue-engineering.” The days are not distant when a patient demanding a liver transplant shall receive an implant of multiple bioprinted micro-particles of liver tissue that are programmed to generate the whole liver inside the body, using the body as a bioreactor! Mankind awaits such three-dimensional surprises.