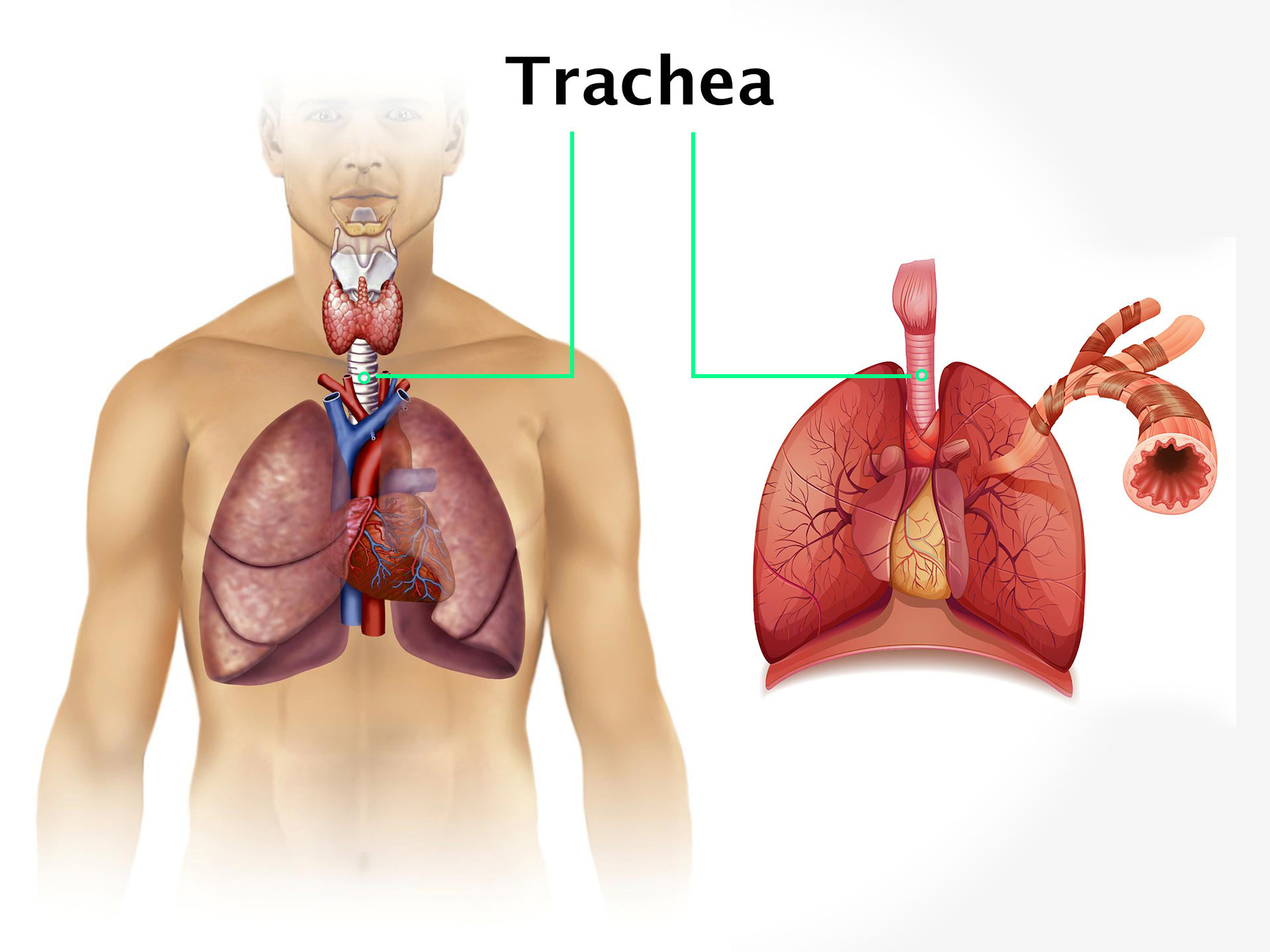
Functions:
In the respiratory system trachea allows the air to flow into the lungs for respiration. The trachea is lined by the goblet cells and ciliated epithelial cells which produce mucus. The mucus moistens the air when it passes through the respiratory tract. It also traps the inhaled foreign particles like dust or bacteria which have escaped the hair of the nasal cavity.
Diseases:
Tracheal diseases and conditions include choking; tracheomalacia means weakness of the tracheal cartilage, mounier-kuhn syndrome which causes abnormal enlargement of the trachea. Tracheo bronchial injury, tracheal collapse, tracheal stenosis means inflammation in the trachea which leads to the scarring and narrowing of the windpipe, tracheo oesophageal fistula is an abnormal channel forms to connect the trachea and oesophagus, tracheal cancer is a very rare condition and tracheal obstruction like tumour or other growth can compress and narrow the trachea.
Interesting Facts:
If water or food enters the wind pipe it may cause choking and difficulty in breathing.