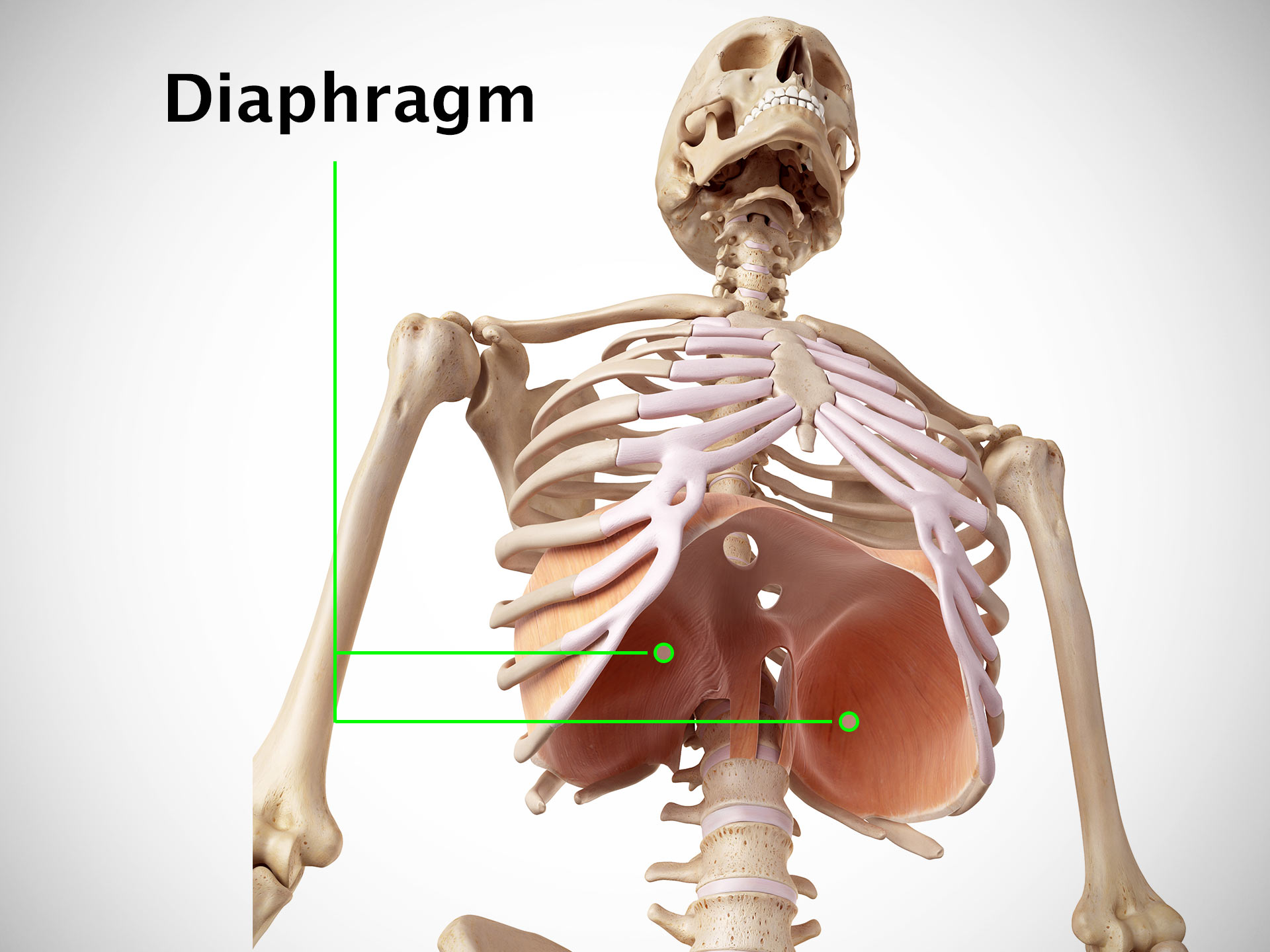
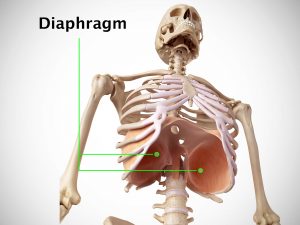
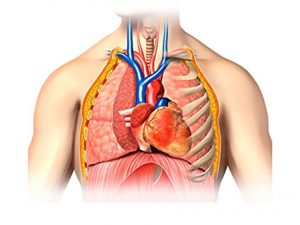
Origin
Ribs and costal cartilages, xiphoid process of the sternum, lumbar vertebrae.
Insertion
All the muscle fibers converge to form the central tendon of the diaphragm.
Blood supply
Superior phrenic artery, inferior phrenic artery, pericardiacophrenic artery, musculophrenic artery.
Nerve supply
Phrenic nerve.
Action
The primary function of the diaphragm is respiration. This muscle is also essential for certain other activities such as vomiting, prevention of acid reflux into the esophagus, and emptying of bowels and bladder.
Disease/Injury
Paralysis of the diaphragm can occur as a result of malignancy, trauma, or other causes leading to nerve compression.
Muscle Exercise
Meditation and other breathing exercises help to strengthen the diaphragm.
Interesting Facts
The diaphragm connects the thorax and abdomen, thus allowing important structures to pass through.