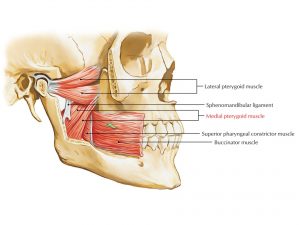
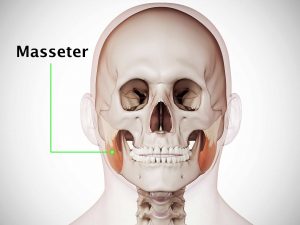
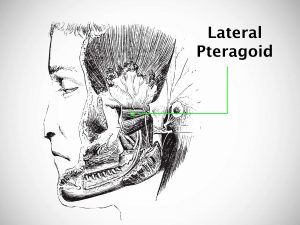
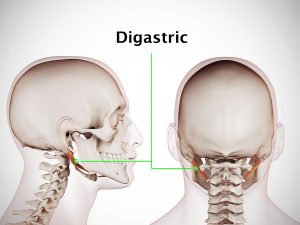
Causes and risk factors
Trauma is one of the major contributing factors. Motor vehicle accidents or collision and sports injuries are the other causes of the avulsed tooth. Severe injury or direct blow on the jaw can also lead to displacement of the tooth. Certain unknown causes also account for 17% of the cases of avulsed tooth.
Clinical presentation:
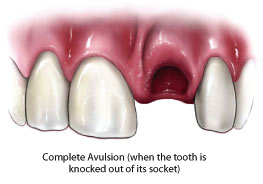
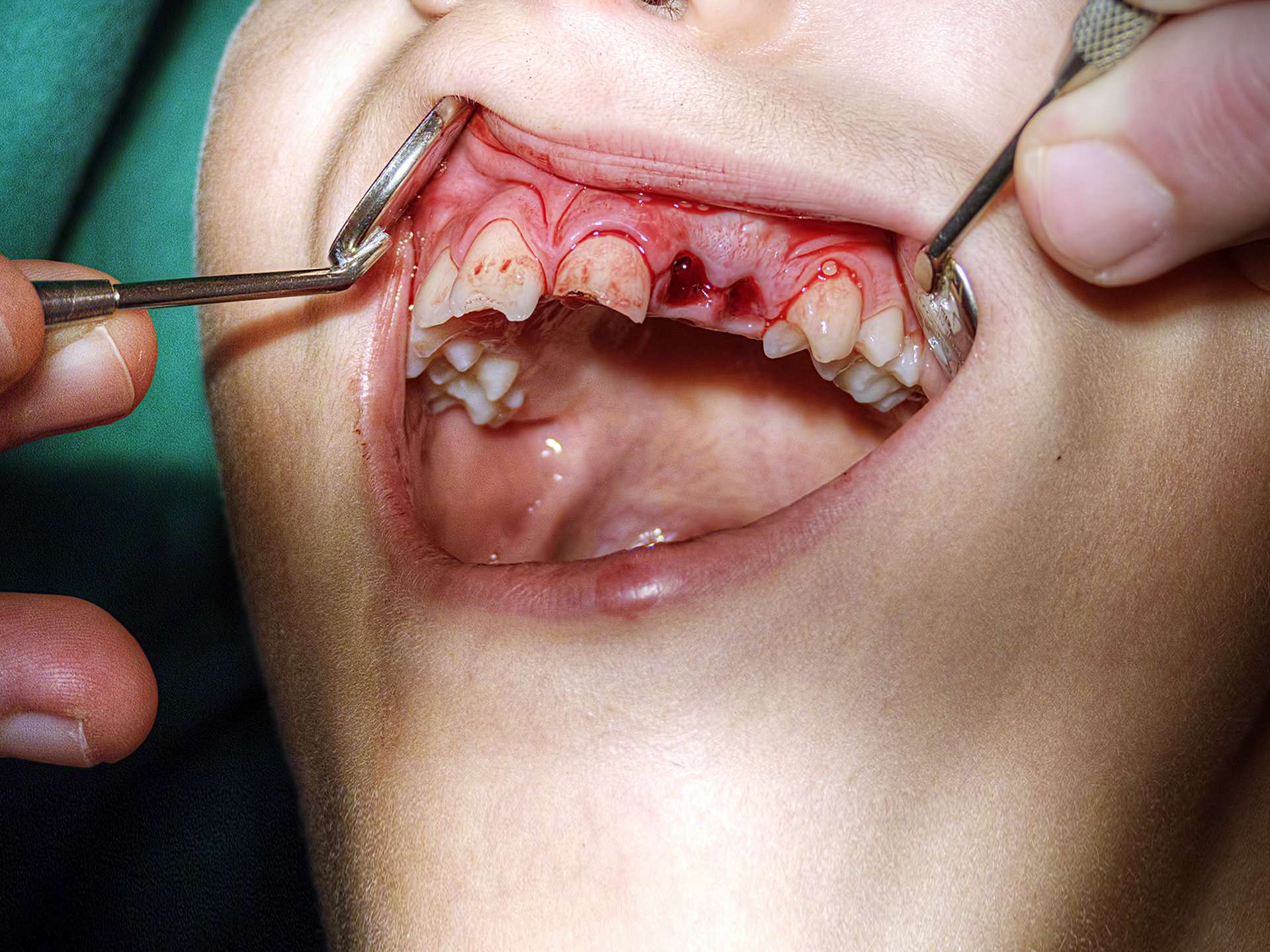
The affected tooth is completely dislocated from the socket. Pain is complained by the patient in the affected area. Bleeding can occur. The sockets of the tooth either appear empty or seem to be filled with coagulum. In case of injury due to direct blow or accident, the tissues surrounding the teeth are lacerated. Discoloration along with swelling of jaw occurs. Cosmetically, an empty socket can hamper the appearance as well as it becomes a favorable place for infection. Over a period of time, this can also lead to misalignment of teeth or can cause pulp infection.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done on the basis of the examination carried out by the dentist and the complaints narrated by the patient. There is often a history of injury. Usually, clinical appearance itself is diagnostic. If the doctor suspects any kind of fracture of the jaw or roots then dental x-ray can be advised.
Treatment:
Avulsed tooth needs to be corrected by dental surgery. The first step which should be adopted is that the roots should not be cleaned or touched and the displaced tooth should be handled at its crown. If possible the displaced tooth must be preserved and carried to the dentist for its reimplanatation. The tooth in such cases must be carried in certain mediums like milk, saline, or hanks solution. Surgery is conducted to reimplant the tooth. Along with this, medication to relieve the pain and antibiotics for preventing infections are prescribed.
Facts and Figures:
Most of the cases of dental trauma are seen between the age of 7-15 years.