Causes and risk factors
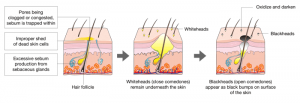
Comedonal acne is caused due to proliferation of the cells lining the sebaceous duct. Along with this, there is increased sebum production. There occurs accumulation of debris which blocks the duct of the sebaceous glands and hair follicle leading to formation of comedo. Certain risk factors also contribute to the formation of comedo. An overhydrated skin is the most common cause. Hence people living in humid climates and tropical regions more commonly suffer from this condition. Smoking, high intake of dietary fats, sugar and dairy products too add up to the causation. Certain hormonal changes have also been responsible for the same. An injury which causes rupture of the follicles like laser treatment on the skin, use of peelers or chemical peels, and squeezing of pimples favor formation of comedo. Irritation of the skin due to use of certain cosmetics, oils, and dyes along with increased sex activity of males hormones are other contributing factors.
Clinical presentation
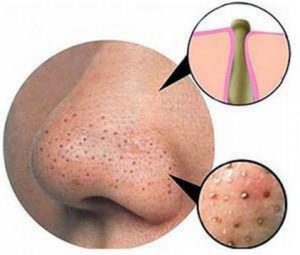
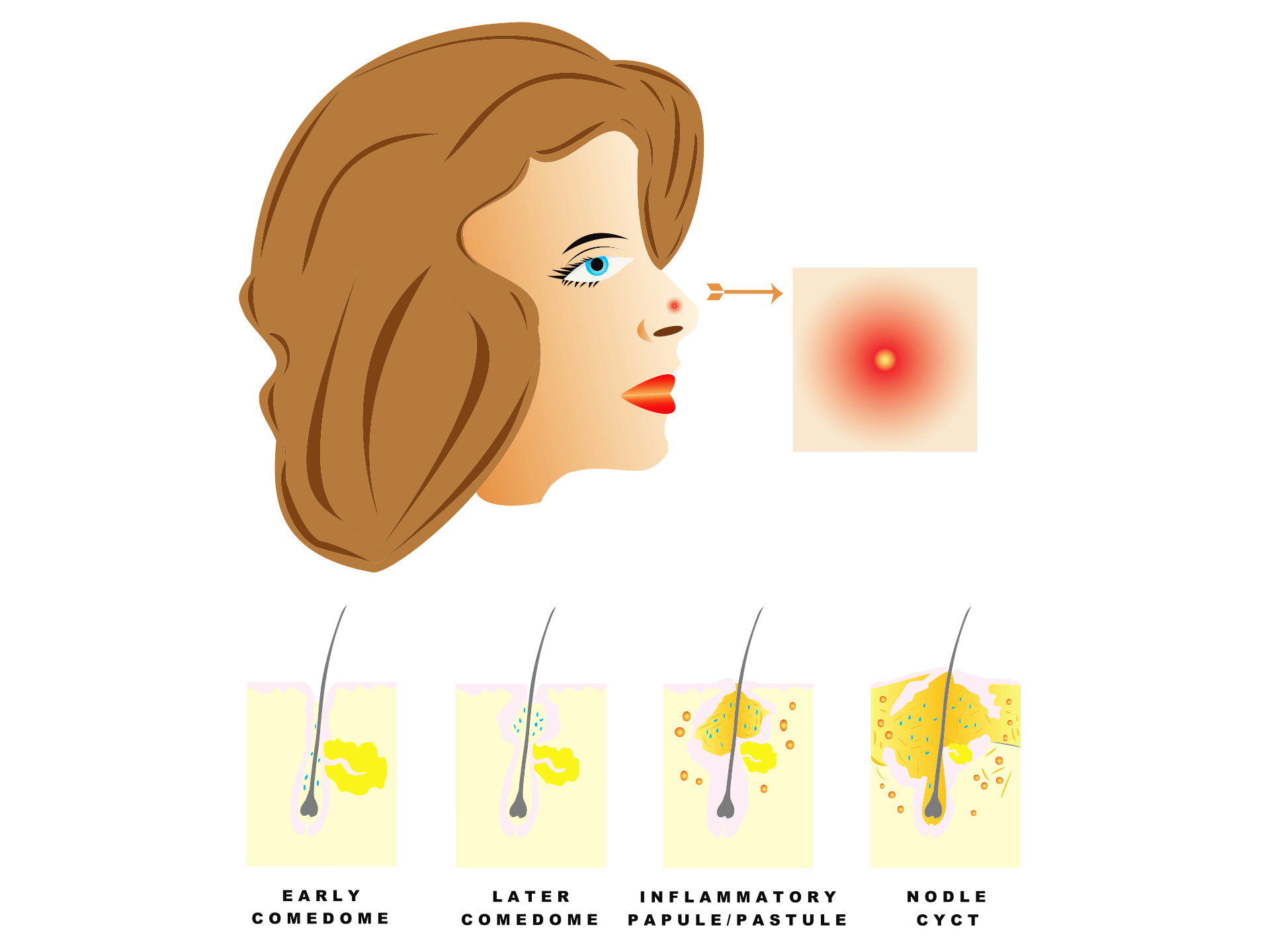
Comedonal acne is of different types – Open variety, closed comedo, microcomedone, macrocomedonal acne, giant type, and solar comedo. Open comedos are commonly known as blackheads. These are small follicles which have dilated openings. The closed variety is commonly known as whiteheads and they have plugged follicles. Microcomedonal acne is small acne which is not easily visible to the naked eyes. While macrocomedonal acne is usually seen on face; these are closed comedos which have a size of more than 2-3 mm diameter. The giant variety is like a cyst with blackhead like opening in the skin. Solar comedos are found on cheeks and chin. This variety is mostly encountered in old people and it is caused due to damage to the follicle due to exposure to sun. Comedos are commonly seen on forehead, chin, and on the nose. These are seen as raised bumps or eruptions. Some are white in color while others have a black appearance. They appear in cluster. These complaints are often mild and do not pose any complaints or sufferings. However, they are a matter of worry from a cosmetic point of view. Negligence and poor hygiene can lead to secondary skin infection.
Investigations
Diagnosis is done on the basis of symptoms narrated by the patient and the examination carried out by the dermatologist. Clinical examination itself is diagnostic. No investigations are needed for diagnosis.
Treatment:
Usually the complaints are mild and do not need any medical intervention. In a few cases, comedolytic topical agents are advised. Where hormonal changes are the causation, hormonal therapy is advised. In some of the cases, if required, antibiotic medications are advised. Use of oil-free cosmetics is recommended. Certain lifestyle changes are necessary which includes stoppages of smoking, low dietary intake of fat and dairy products. It is advised to wash the face twice daily. In rare cases, other modes of treatment can be used. Either cryotherapy or electrosurgery can be done.
Other modes of treatment:
Certain other modes of treatment can also be helpful in coping up the symptoms. Taking into consideration the symptoms in a holistic way, homoeopathy can offer a good aid for the relief of the symptoms. The Ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbs and synthetic derivates can also be beneficial in combating the complaints.