Causes and risk factors
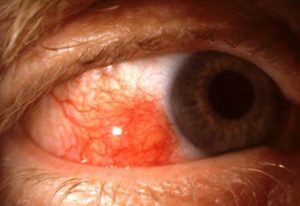
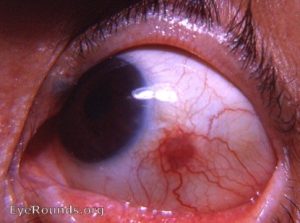
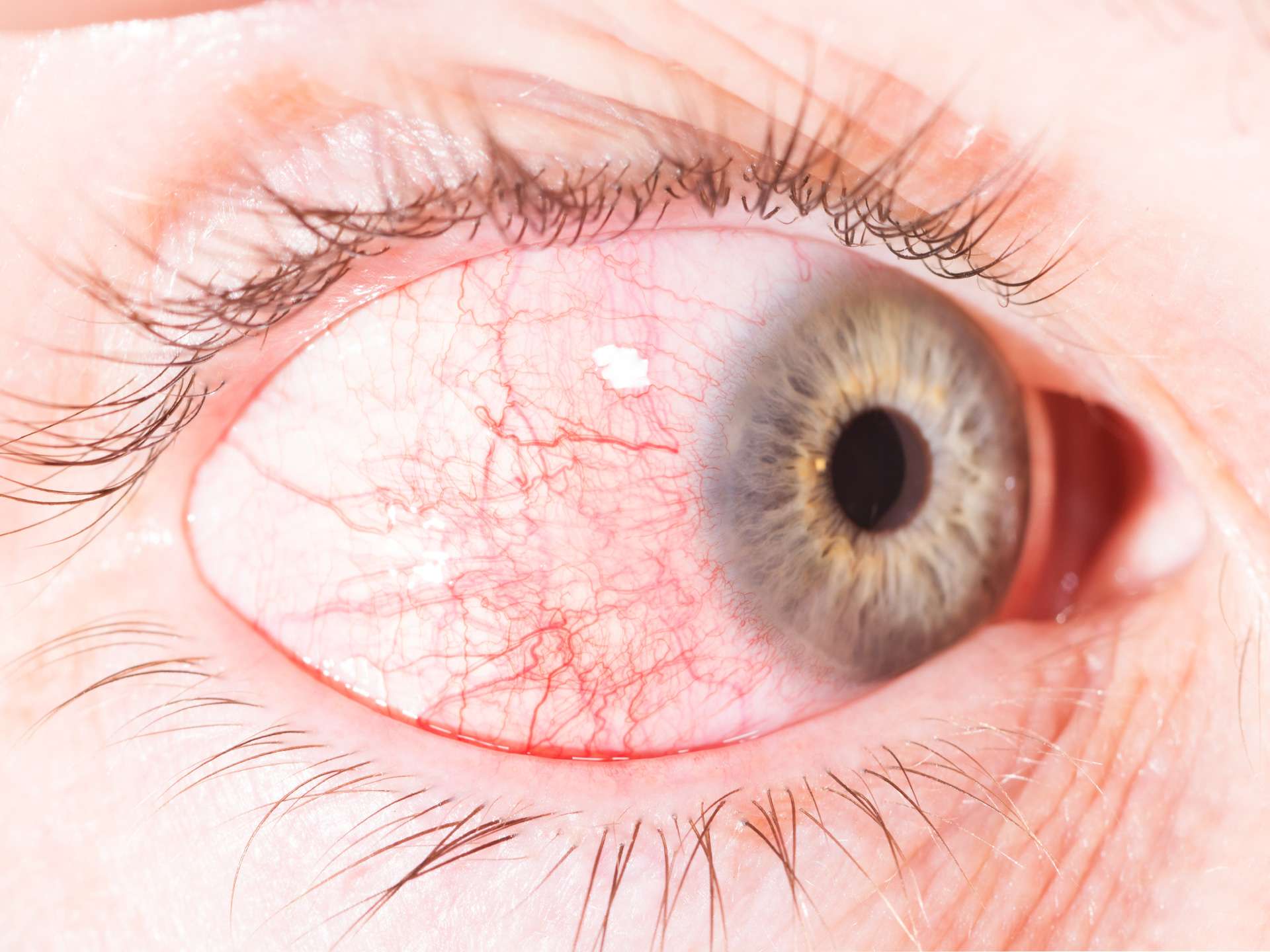
Episcleritis are of two types – Diffuse which involves the entire episclera, and nodular – it involves only a small circumscribed area. There is no definite cause, but it can be associated with the following disease conditions – rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, gout, Sjogren’s syndrome, syphilis, and tuberculosis.
Clinical presentation
Patient presents with eye pain, red appearance of the eye, watering of the eyes, and sensitivity to light.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the ophthalmologist helps in diagnosis. Ophthalmoscopy examination is done.
Treatment
In most cases, no treatment is required as it is self-limiting. Some severe cases may require corticosteroid eye drops and oral NSAID medications.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating episcleritis. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly, the Ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates is also found to be effective in treating episcleritis.
Image 1 Image 2