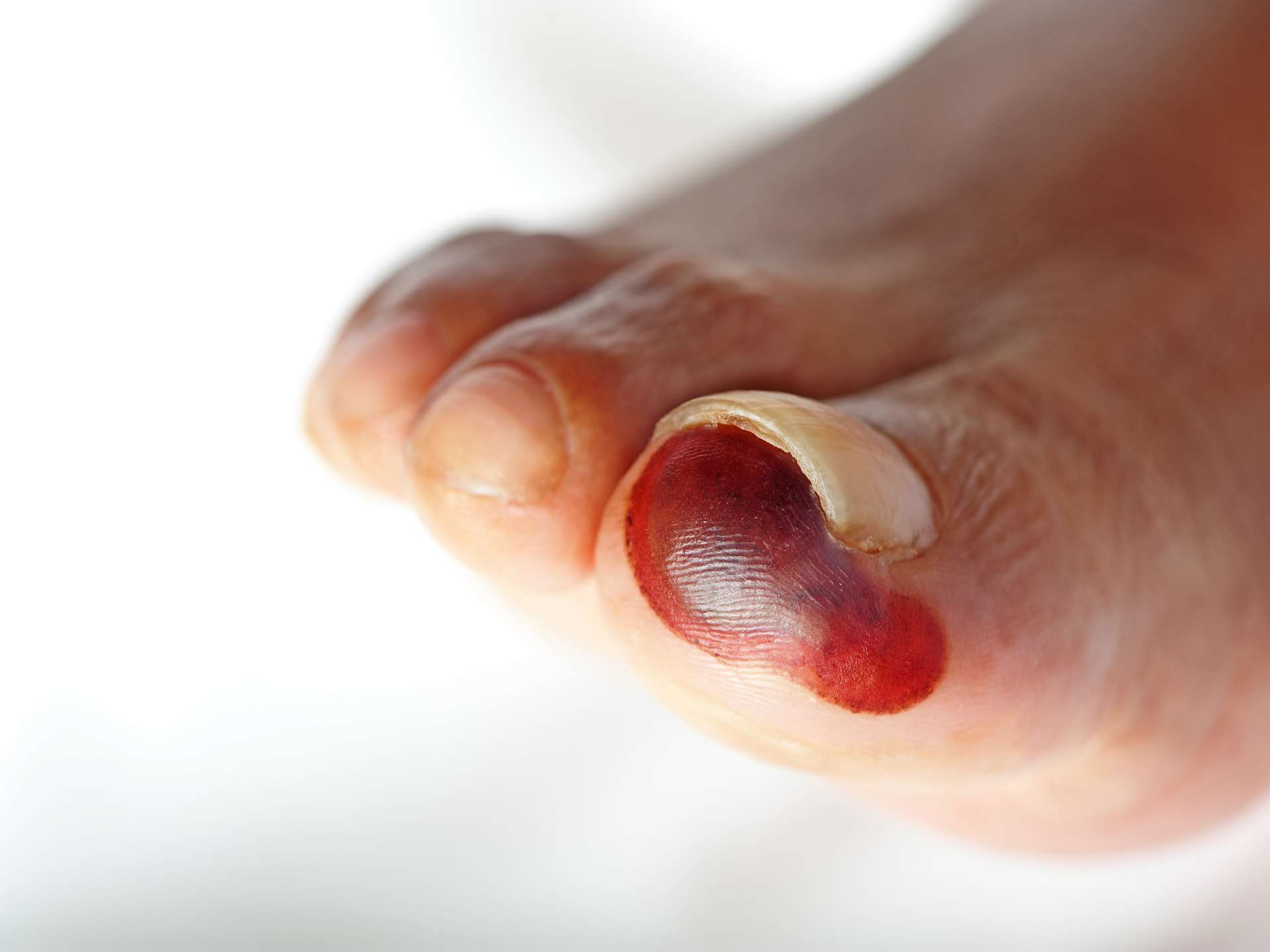
Causes and risk factors
Gangrene is the result of insufficient blood supply to the organ or the tissue. Types of gangrene are dry, wet, and gas gangrene. All body tissues and organs receive oxygen thorough blood. If any part fails to receive oxygen due to insufficient blood supply, it starts dying, leading to the condition called dry gangrene. Dry gangrene is characterized by dry and shriveled skin ranging in color from brown to purplish-blue to black. The onset and development is very slow. Wet gangrene occurs due to bacterial infection of body tissues. The tissues react to the presence of the bacteria by growing moist and breaking down. Wet gangrene spreads rapidly. Gas gangrene is caused by Clostridia bacteria and affects deep muscle tissues. It develops in an injury or surgical wound that is deprived of blood supply. There is formation of gas bubbles and toxins inside the affected area thus called as gas gangrene. The diseases and conditions that are associated with a higher risk of developing gangrene are arteriosclerosis, Raynaud’s disease, diabetes, hernia, appendicitis, presence of blood clots, reduced immunity due to certain diseases or treatments, history of recent surgery, history of recent trauma [especially where body tissues are crushed], frostbite, burns, animal bites, etc. , indulging in alcohol, smoking, or intravenous drug use, etc.
Clinical presentation
Dry gangrene develops slowly. It commonly occurs in elderly patients with atherosclerosis. A red line appears on the skin which differentiates the affected tissues from the healthy ones. There may be slight or no pain at all. The affected area changes from red to brown to black. The area becomes dry, shriveled, cold, and numb and eventually falls off. Wet gangrene occurs due to a bacterial infection in tissues affected by an injury – a severe burn, frostbite, etc. It is also common in diabetic patients. It spreads very rapidly and can be fatal. The affected area swells and the skin color changes from red to brown to black. Fever, pus formation, and a foul smell may be present. The symptoms of gas gangrene develop rapidly and spread quickly. There is presence of toxic gas formation under the skin due to release of toxins by bacteria and death of muscle tissue. Skin shows blisters filled with brown-red fluid. Foul-smelling brown-red or bloody fluid drains from the tissues. Patient experiences pain around a skin injury. Skin color is pale, which later becomes dark red or purple. There is increasing swelling around a site of injury. Associated signs and symptoms include tachycardia [increased heart rate], fever, sweating, yellow discoloration of the skin [jaundice].
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Microscopic examination of affected tissue or fluid from blisters to check for bacteria is done. Complete blood count is recommended. Imaging studies such as x-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans to check the spread of gangrene in the internal tissues are advised. Arteriogram may be done to detect whether there is blockage in the arteries.
Treatment
Medical treatment involves antibiotics that are prescribed in cases of wet and gas gangrene. Hyperbaric oxygen chamber is useful to provide an oxygen-rich environment for slow progression of gas gangrene. Surgery involves one or more of the following – debridement of the dead tissue; reconstruction of the affected area with the help of skin grafts; amputation of the affected limb or body part; vascular surgery to improve blood supply. Prevention of gangrene is possible by good diabetic care. Prompt treatment of any wounds, precautionary measures against development of frostbite. Avoidance of use of tobacco, alcohol, intravenous substance abuse, etc., will contribute further to the treatment.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating gangrene. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly, the Ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates is also found to be effective in treating gangrene.