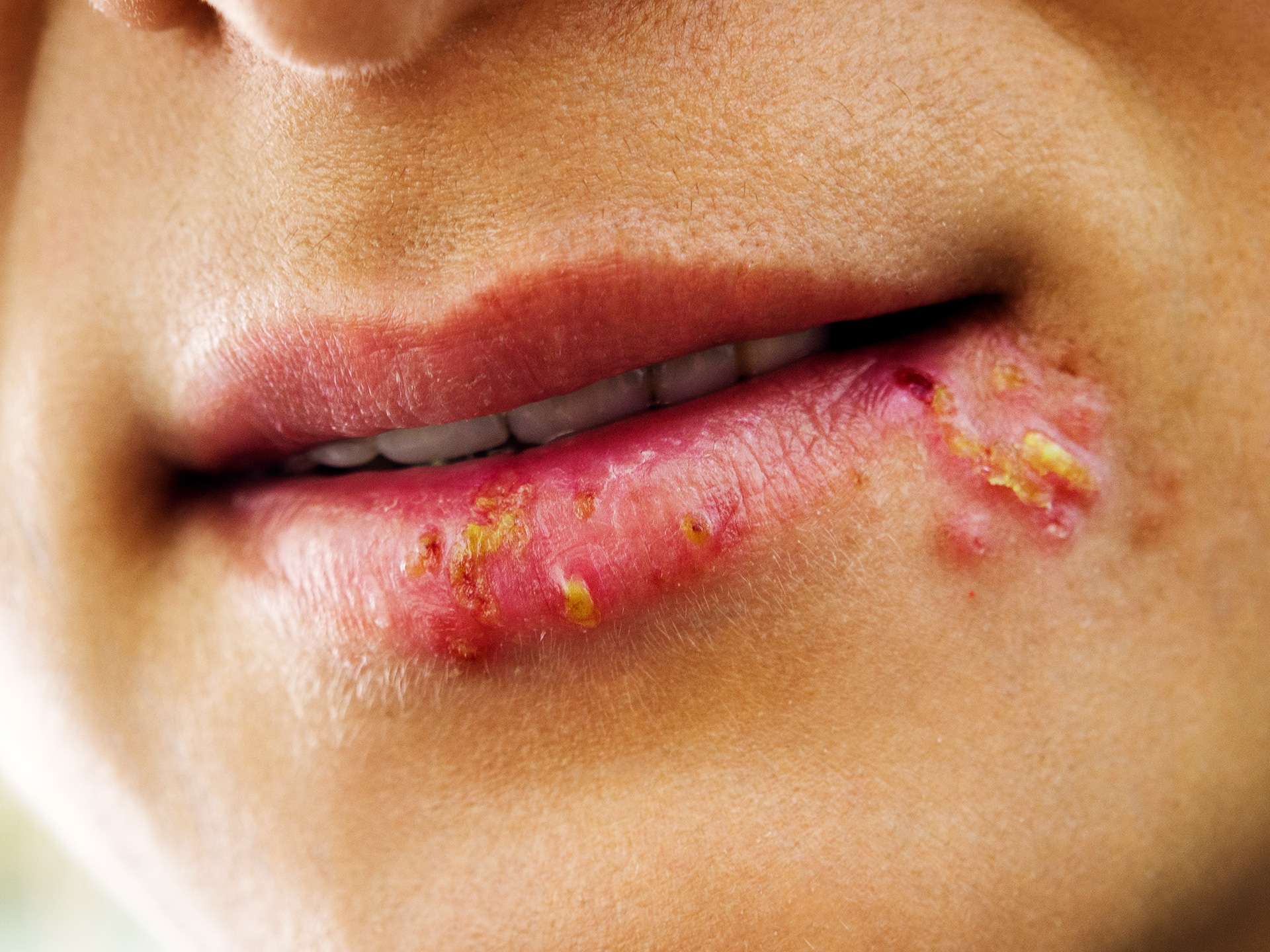
Causes and risk factors
Herpes simplex is caused by herpes simplex virus [HSV]. There are 2 types of herpes simplex viruses. HSV–1 also called as oral herpes; it can cause cold sores and fever blisters around the mouth and on the face, though it can spread to genital area during oral sex. The virus can spread with general interactions such as eating from the same vessel, sharing a lip balm, or kissing. HSV-2 virus is generally responsible for genital herpes. The virus spreads through sexual contact and skin-to-skin contact. It is highly contagious. It can also cause oral sores. Risk factors for herpes include having multiple sex partners, being female, having another sexually transmitted infection, or weak immune system.
Clinical presentation
Many people who are infected with herpes simplex virus may not have signs and symptoms, but they may still transmit the virus. Symptoms include blisters, sores in the mouth, or on the genitals with itching. Symptoms similar to flu are seen, which include fever, swollen lymph nodes, headaches, tiredness, lack of appetite. Pain during urination is experienced in case of genital herpes. Herpes simplex affects other parts like skin, eyes, etc., the virus spreads to eyes, causing herpes keratitis. The symptoms of herpes keratitis include, eye pain, discharge, and a gritty feeling in the eye. Factors that may trigger outbreaks of this infection include stress, fatigue, illness, recent surgery, menstruation, lowered immunity such as in disease like HIV. Neonatal herpes can be caused in the newborn due to exposure to HSV1 or HSV-2 from genital tract to neonate during delivery.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Herpes culture, DNA tests are done. Blood tests to check for antibodies to HSV-1 and HSV-2 is recommended.
Treatment
The goal of the treatment is to treat the sores. Anti-viral medications are given which may reduce the risk of spreading the virus to other people and lower the intensity of the outbreak of this infection. Analgesics and antipyretics are given for symptomatic relief. Prevention of herpes simplex is possible by practicing safe sex, avoiding oral sex.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating herpes simplex. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly, the Ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates is also found to be effective in treating herpes simplex.
Facts and figures
400 million people worldwide are affected by HSV-2.