Causes and risk factors
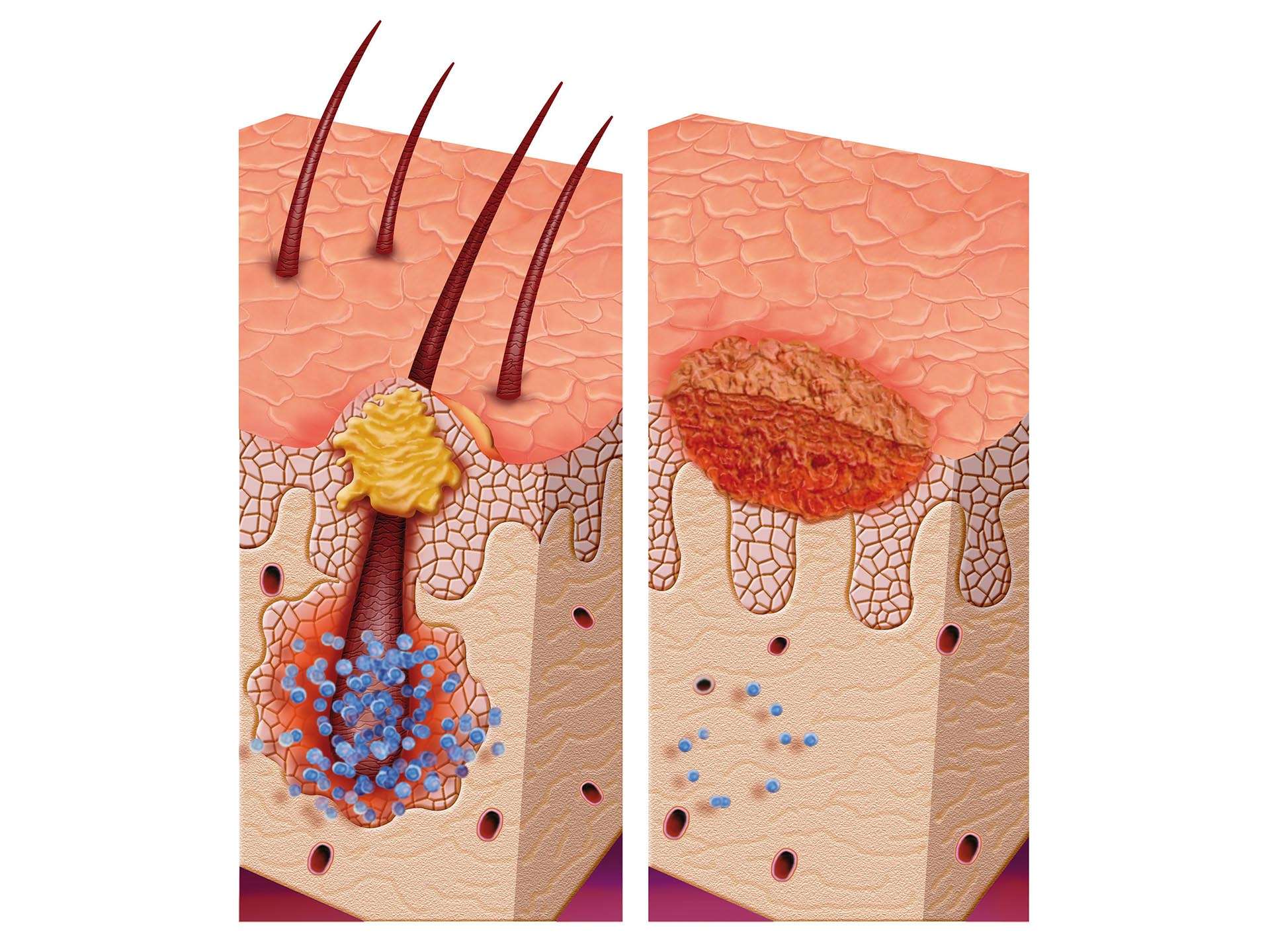
The exact mechanism and cause is still not clear about scalp folliculitis; however, infection caused due to micro-organism is one of the triggering factors. It is said to be an inflammatory reaction of the hair follicle. The major contributing micro-organisms are bacteria, yeast, and mites. Certain skin infections particularly the dermatitis and psoriasis can also trigger this infection. A person with low immunity is more prone towards such an infection, mainly those suffering from HIV and diabetes. Prolonged use of tight caps or sweaty helmets on scalp, certain irritating substances like hair dye or some oils along with poor hygiene are certain other contributing factors.
Clinical presentation:
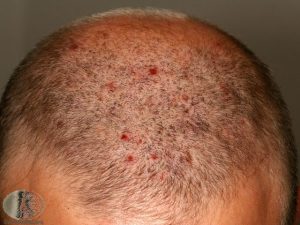
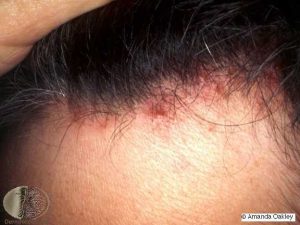
The complaints are seen for a few days to weeks after contact with the micro-organism and are mild. In certain cases, however, they can be severe. Either the entire scalp or particularly the forehead and vertex region can be affected. The patient presents with complaint of redness of the affected area. Itching and small eruptions which are filled with pus or blood (pustules) are the characteristic features seen. Severe itching can lead to oozing of the blood or pus. On the contrary, itching itself can aggravate the complaint and give way to secondary infections.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done on the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the physical examination carried out by the dermatologist. History of the patient is taken into consideration to elicit any contributing. Routine blood test, blood culture, or testing of the discharge is often diagnostic.
Treatment:
Usually in a few weeks the complaints resolve, however, if they persist, the dermatologist can recommend certain oral antibiotic medications. Application of topical antibiotics can also be advised. In severe cases, topical steroids are suggested. In cases where the complaints are recurrent, laser hair removal therapy is found to be effective. Use of shampoo or antidandruff shampoo containing mild antimicrobial properties is advised.
Complications:
Scalp folliculitis is a self-limiting disease and rarely can lead to certain complications. In some cases, however, the eruption can enlarge and lead to formation of carbuncles and furuncles. Cellulite is a rare complication. Post-inflammatory hypopigmentation is commonly seen as the complaint resolves.
When to contact a doctor:
If anyone suffers from redness along with severe itching of scalp, contacting a dermatologist is advised.
Prevention:
Maintenance of good hair care is essential. Avoid use of irritating substances. Mild shampoos must be used. Avoid sharing personal things.
System involved: Integumentary system
Organ involved: Skin, scalp
Image: