Causes and risk factors
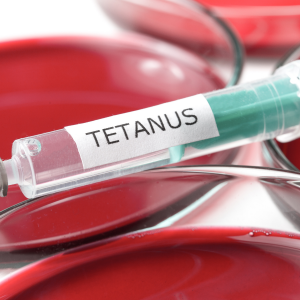
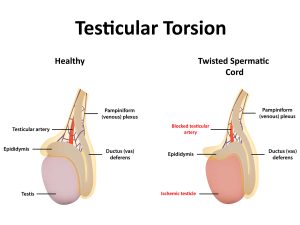
Although testicular torsion can take place at any age the incidence is high in boys between the ages of 10-25 years. In testicular torsion the spermatic cord is twisted or turned around the testis. Bell clapper deformity is one of the major causes of testicular torsion. Under normal condition the testis are attached to the scrotum which restricts its free movement, however in cases of bell clapper deformity the testis can move about freely thus increasing the chances of testicular torsion. The twisting of the spermatic cord around the testis can also occur due to strenuous exercises or any injury to the testis or scrotum.In some cases testicular torsion also occurs without any apparent cause. It can also occur anytime during sleep or even during standing or sitting. Athletes are more prone for developing testicular torsion.
Clinical presentation:
In most of the cases left sided affection is more commonly seen. Most of the cases one sided testis are involved, in rare cases bilateral affection occurs. The patient comes up with complaints of sudden pain and discomfort in the scrotal area. Mostly the pain is one sided. The pain can last for hours or days .Nausea and vomiting occurs. The patient experiences difficulty and pain while passing urine, burning during urination occurs. Swelling of the testis is seen and the overlying scrotal skin becomes red. It is tender on examination. Untreated torsion can lead to infarction and atrophy of the testis.
Investigations:
The diagnosis is confirmed on the basis of the symptoms narrated by the parents and certain physical examination is carried by the doctor. Usually the physical examination is sufficient to confirm the diagnosis. Color Doppler and Ultrasound scan studies can be helpful in confirming the torsion. Certain other sets of investigations like routine blood test, urine analysis and blood sugar levels etc can also be advised.
Treatment:
It is an emergency condition. Depending upon the degree of torsion the treatment can be planned. Anti-inflammatory and analgesics medications are administered. In some cases the de twisting can be done manually (manual distortion) while in some cases surgical repair is needed. In cases where the surgery is neglected it can lead to gangrene or infarct.