Causes and risk factors
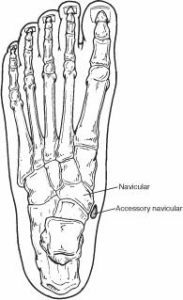
The presence of extra navicular bone is congenital. This bone is integrated with the posterior tibial tendon. Certain factors can trigger the bone complaints. Trauma is one of the major contributing factors for this. Microtrauma caused due to repeated activity or due to overuse of the muscle can also cause irritation of the bone. Tight shoes can cause pressure on the bone leading to pain. Accessory navicular syndrome is most commonly seen in patients who have a flat foot. The incidence is more commonly seen in females.
Clinical presentation:
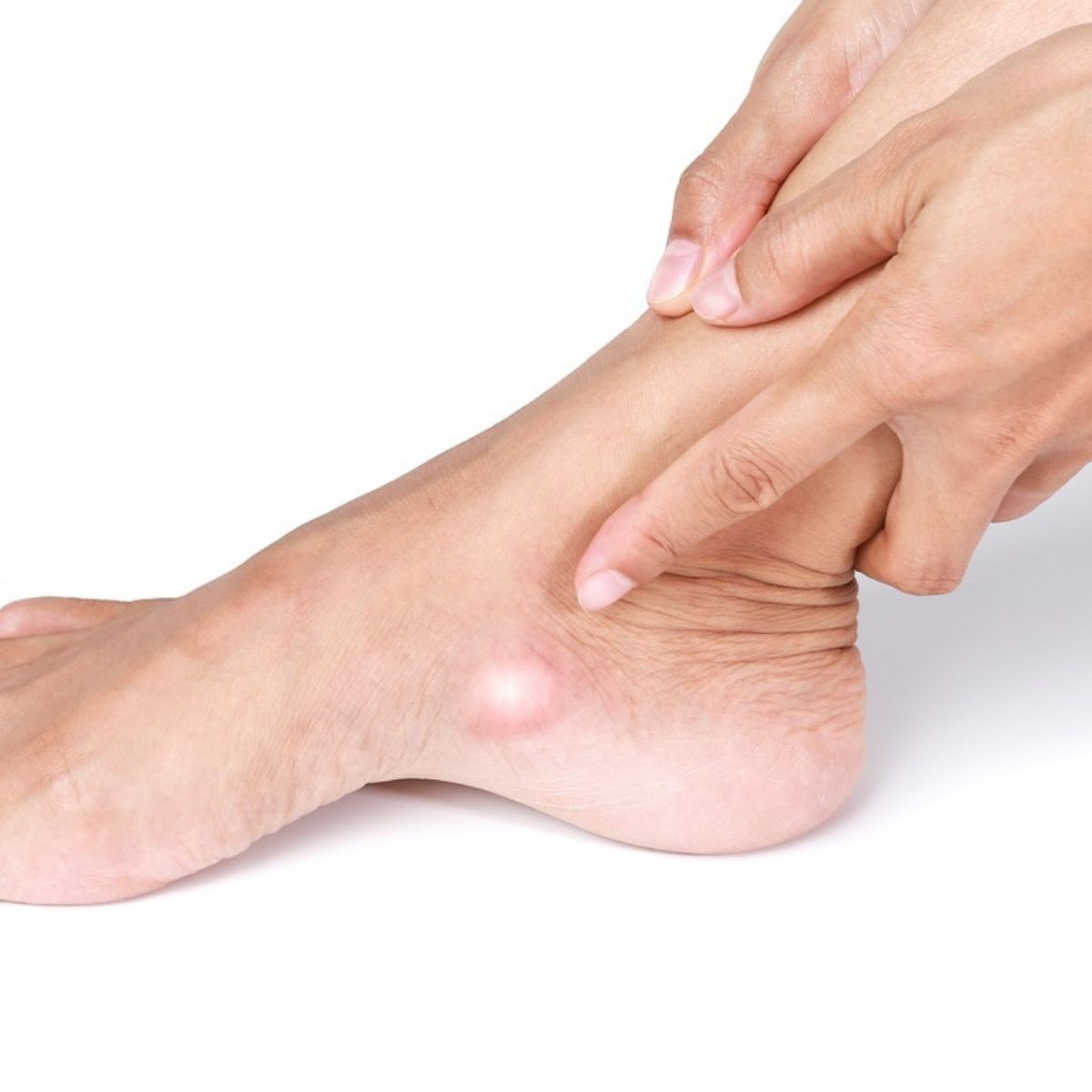
Depending upon the location of the bone, the accessory navicular syndrome is classified into three types: Type I: The accessory navicular bone is situated at a small distance (<3 mm) from the navicular bone. Type II: The accessory navicular bone is situated at a distance of 1.2 cm from the navicular bone. Type III: The accessory navicular bone is fused with the navicular bone. Although the bone is present since birth, the complaints occur during adolescence. The complaints are mostly bilateral. Pain is the prominent feature that is seen at the inner side of the foot just above the arch. It is dull and throbbing type of pain. It is aggravated by activity and is better on rest. A bony prominence is felt on touching. Slight swelling can also be seen. On examination of the foot, tenderness is seen. Plantar fasciitis, heel spur, and development of bunions are some of the common complications seen.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done on the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the physical examination carried out by the orthopedic doctor. Plain x-ray is usually sufficient for diagnosis, if needed CT scan or MRI scan can be done.
Treatment:
Rest and restriction of movement is the first step involved. Analgesic or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are advised by the orthopedic doctor. Icepack application can be advised which will help to relieve the swelling. Orthotic devices like shoes which will provide support for the arch are suggested. If the conservative treatment fails to be effective, then surgical means can be used. Surgery consists of removal of the extra bone or repair of the posterior tibial tendon. Post surgery, certain physical exercises are advised to improve flexibility and strength of muscles.
Other Modes of treatment:
Certain other modes of treatment can also be helpful in coping up with the symptoms. Taking into consideration the symptoms in a holistic way, homoeopathy can offer a good aid for the relief of symptoms. The Ayurvedic system of medicine, which uses herbs and synthetic derivates, can also be beneficial in combating the complaints. Certain yoga exercises can also be helpful in strengthening the muscles.
Facts and Figures:
Almost 10% of the population suffers from this complaint.