Causes and risk factors
The exact mechanism and cause about acne fulminans is still not clear. Various hypotheses have been postulated. One of the theories suggests that there exists a relation between androgens circulating in the body; however, the mechanism is not known. Initiation of isotretinoin therapy, anabolic steroids, and testosterone is said to be one of the contributing factors. Another hypothesis suggests that it is an autoimmune reaction of the body; certain genetic causes have also been put forth. Studies have suggested that it may also be caused due to hypersensitive reaction to the surface bacteria.
Clinical presentation:
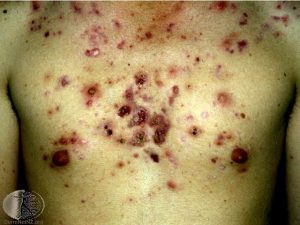
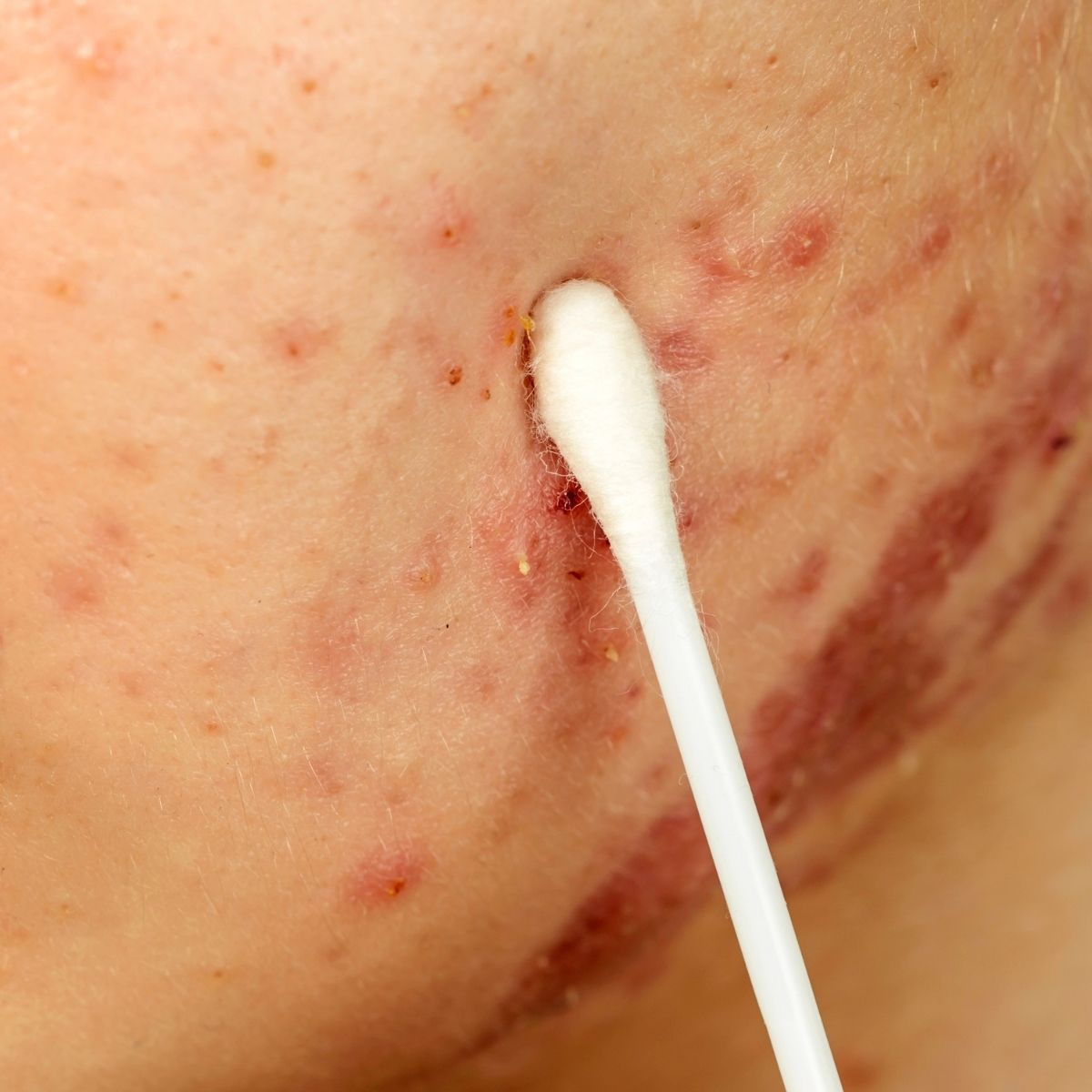
The most common site of affection is the back and chest. Appearance of nodules is the characteristic feature seen. The complaints appear suddenly. These nodules undergo suppuration rapidly, causing appearance of ulcers which bleed easily. These further lead to osteolytic lesions in the bones. The affected area becomes inflamed leading to itching, pain, and soreness. Along with these skin complaints the patient also suffers from certain systemic complaints. Fever, malaise, tiredness, pain in various muscles (myalgias) and various joints (arthralgia) are complained by the patient. Along with weight loss due to loss of appetite, enlargement of liver and spleen is seen. Along with all these, various laboratory examinations carried out shows abnormality.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done on the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the physical examination carried out by the dermatologist. Routine blood test, blood cultures or testing of the discharges along with histological examination is often diagnostic. This condition is characterized by increased WBC, low hemoglobin, and increased ESR. C- reactive protein test is done which is positive along with x-rays of bone done suggests osteolytic lesions.
Treatment:
The dermatologist can recommend certain oral antibiotic medications. Application of topical antibiotics can also be advised. In severe cases, topical steroids along with systemic corticosteroids are suggested. Administration of anti-inflammatory drugs is another choice of medications.
Complications:
Osteolytic lesion in bones, polyarthritis, and hypopigmentation post inflammatory pigmentation is seen.
When to contact a doctor:
Recommendation of an expert in the field of dermatology is advised in cases where the patient suffers from complainant of skin eruptions along with itching and ulcer formation.
Prevention: As the exact cause is not known, it is difficult to elicit the preventive measures.
System involved: Gastrointestinal tract, musculoskeletal system, integumentary system.
Organ involved: Skin, bone, muscles, liver, and spleen.