Causes and risk factors
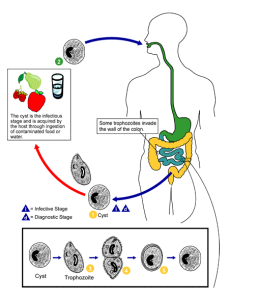
Balantidiasis is caused due to the infection with protozoa Balantidium coli. It is transmitted through fecal-oral route by contaminated food and water.
Clinical presentation
Balantidiasis can be asymptomatic or can produce symptoms like several loose stools in a day, tenesmus, epigastric tenderness, nausea, abdominal pain, sudden weight loss, weakness. Chronic infection can cause loose stools alternating with constipation, epigastric tenderness, colicky abdominal pain, mucus in stools.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. The diagnosis of balantidiasis is confirmed by microscopic stool examination for protozoa Balantidium coli.
Treatment
No treatment is required for asymptomatic patients. Medical treatment includes antibiotics, analgesics. Balantidiasis can be prevented in following ways like proper handling of food, maintaining personal hygiene, purification of drinking water, avoiding eating raw or undercooked food, proper disposal of human waste.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating balantidiasis. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly, the Ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating balantidiasis.