Causes and risk factors
Ultraviolet rays from excessive sun exposure or from tanning is the most common cause of basal cell carcinoma. Exposure to arsenic or radiation causes BCC. People with weak immune system are at risk of developing basal cell carcinoma. Family history of BCC is important predisposing factor. Other contributing factors include open sores that resist healing, chronic inflammatory skin conditions, complications of burns, scars, vaccination, tattoos.
Clinical presentation
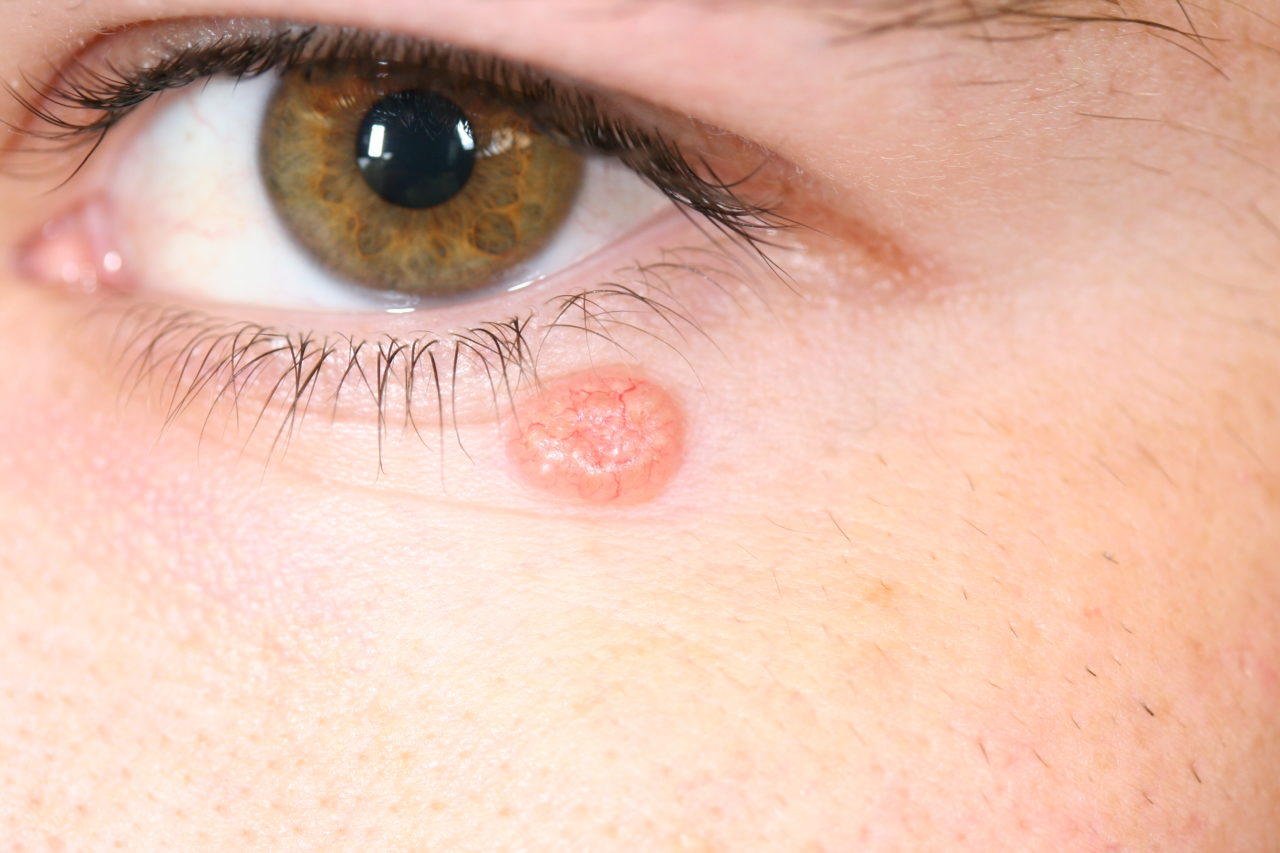
The lesions of BCC present like open sores, red patches. Dome shaped, red coloured, waxy bump with visible blood vessels inside. Lesions can be pink, skin-colored, brown or black. They are fragile and can bleed easily. The lesions can be mistaken for a patch of eczema. BCC can present as an open sore which remains open for few weeks, heals and again bleeds. A persistent non healing sore is an alarming sign of BCC. It can be seen as an irritating erythmatous patch found on face, chest, shoulder, arms or legs that itches. There may be crust formation. A shiny bump or a nodule, which is pearly and translucent. It is white, pink or red in color. It may be blackish brown and can be mistaken for a mole. BCC can also be presented as a pink colored circular growth on skin which has elevated borders. It is depressed in the centre. The lesion grows and develops tiny blood vessels gradually. A scar like white or yellow patch can be seen on skin. It is waxy and has undefined borders. It is a sign of invasive BCC. It is much extensive than seen on the surface.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Skin biopsy is recommended for the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment involves excision in cases where there is large basal cell cancer. The affected area is removed along with surrounding normal skin. Curettage and electrodessication involves scrapping away the tumor and then destroying remaining cell using electric needle. Mohs surgery involves removing the cancer cells layer by layer and examining each layer under the microscope until no abnormal cells remain. Cryosurgery consists of using liquid nitrogen to freeze cancer cell, which eventually die. Radiation therapy is indicated when surgery is not possible. Photodynamic therapy uses light to remove early cancer cells. Supportive care is given such as medicated creams are used to treat certain basal cell carcinomas that are limited to the surface of the skin. Medications are used in cases where the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating BCC. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating BCC.