Causes and risk factors
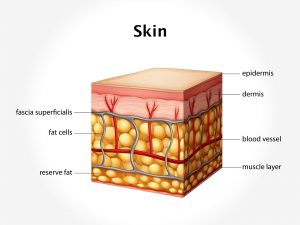
Chrysiasis is caused due to deposition of gold particles in the upper dermis of the skin. It is commonly seen because of prolonged use of gold therapy that is used in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. This therapy has also been used as a therapeutic mode in tuberculosis. However, the incidence of this condition is greatly reduced in current era as the newer drugs which are much effective and have fewer side effects are being used.
Clinical presentation:
The characteristic feature of chrysiasis is bluish purple discoloration of skin. Apart from this, the patient has no complaints. This discoloration is commonly seen in areas which are exposed to light. The other common site affected is sclera. Complaints are seen a few months after the initiation of treatment.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done on the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the physical examination carried out by the dermatologist. There is often a history of administration of gold therapy. Examination of affected tissue under light microscope or electron microscope along with spectroscopic examination is diagnostic.
Treatment:
The condition is irreversible and yet there is no effective treatment available for this condition.