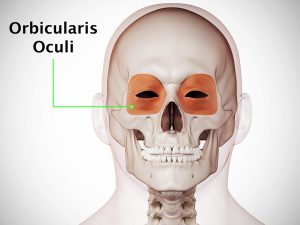
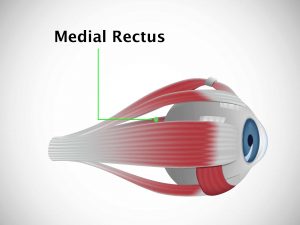
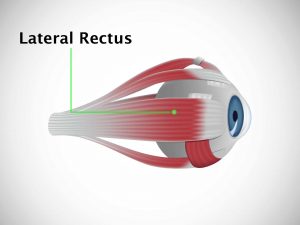
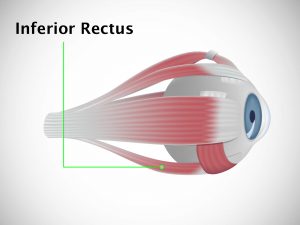
Causative & risk factors
Farsightedness occurs due to abnormal curvature of the cornea or lens of the eye. This condition tends to run in families and is usually present since birth.
Clinical presentation
The affected person can clearly visualize far away objects, whereas objects nearer to him appear blurred. In order to see clearly, the person may have to squint. Aching or burning in eyes, headache and other symptoms of eyestrain may be present.
Investigations
Farsightedness is diagnosed by carrying out an eye exam.
Treatment
Farsightedness can be easily corrected using spectacles or contact lenses, designed to suit the refractive error of the patient.
Surgical correction of the corneal curvature is also an available option. The available surgical options are Laser-assisted in-situ keratomileusis (LASIK), Laser-assisted subepithelial keratectomy (LASEK), Photorefractive keratectomy and Conductive keratoplasty.