Causes and risk factors
The exact cause of pituitary tumor is not known. A strong familial history and certain genetic factors are some of the contributing factors. The cells they undergo an uncontrolled and abnormal proliferation. The cause of uncontrolled proliferation of cells is not clear.
Clinical Presentation
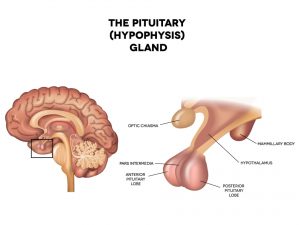
The tumor can be of variable size. They can either be benign or cancerous. The Benign tumor is also of two types functional and non functional. Functioning tumors are those which produce hormones while those who do not produce hormones are called as non functioning. As per the size of the tumors, they are classified as Macro adenoma (size is > 10mm) and Micro adenoma (size is < 10mm). Cases of pituitary tumors which are malignant are rare. Initially when the size of the tumors is small the patient can remain asymptomatic, changes in the various hormone levels occur initially which are accidentally detected. As the size of the tumor increases and it starts moving outside the sella, it leads to compression of the nerves. This results in variety of symptoms like headache, partial blindness, nausea and vomiting. Increase in blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, menstrual irregularities are seen. Depression, anxiety, seizures and impotency can also occur.
Investigations
The diagnosis is done on the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and physical examination. Various scans of the brain like CT or MRI are diagnostic. Certain other investigations like routine blood test, lipid profile, renal and liver function test, blood sugar levels can also be done. If required thyroid function tests are suggested. Measurement of hormone levels in the blood can also be done.
Treatment
The treatment aims at reducing the size of the tumor and normalizing the hormonal levels. Administration of a dopamine agonist is the first line of treatment. Surgical intervention consists of Transcranial or transphenoidal approach for removing of the tumor. Radiation therapy is also another line of treatment. If after surgery the growth hormone levels remain high the somatostatin drugs are given.
Other modes of treatment:
Certain other modes of treatment can also be helpful in coping up the symptom. Taking into consideration the symptoms in holistic way, homoeopathy can offer a good aid for the relief of the symptoms.