Causes and risk factors
Vulvitis may be caused due to certain infectious or noninfectious factors. It can be caused due to infection, allergy, or injury. Infection caused due to bacteria, fungi, or yeast is the most common cause. Sexual intercourse is the most common medium of spread of infection. Infection of the pubic hair also transmits the infection to the folds of skin of vulva. Although this condition can affect women at any age, it is more commonly seen in postmenopausal women or in girls before puberty. The cause is still not clear, but it is possibly thought that the low levels of estrogen are the contributing factors. Uncontrolled diabetes, intrauterine device implantation, or allergy to certain medications and steroids can also lead to inflammation of the vulva. Use of tight fitting, unclean, or damp innerwear, use of vaginal deodorants or sprays, douching, horseback riding, rubbing on bicycle seat all can cause irritation of the sensitive area. Poor vulval hygiene is a major contributing factor.
Clinical presentation:
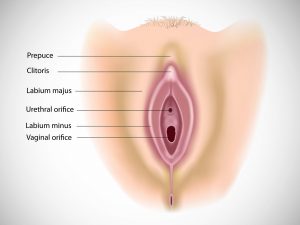
Redness of the vulval folds, itching, burning, and discharges are the cardinal symptoms of vulvitis. The discharges are offensive. The women complain of pain or burning during micturition. Dyspareunia (painful coitus) is the other symptom which the patient comes up with. On examination, swelling and redness of skin fold or vulva can be seen. In severe cases, fluid filled eruptions or thick white patches can be seen.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done on the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the physical examination of the vagina carried out by the gynecologist. Along with vaginal, per rectal examination is also done. In order to confirm the diagnosis, certain investigations can be advised. Testing of the discharge is suggested. Routine blood test, urine routine, and ultrasonography or the abdomen and pelvis are other investigations suggested. In severe cases, a Pap test is also suggested.
Treatment:
Depending upon the cause, medications are prescribed. Anti-bacterial or anti-fungal medications in form of oral or topical for bacterial and fungal infections respectively is advised. For noninfectious form, estrogen or hydrocortisone in the form of cream or tablet is suggested. Sitz bath can also be recommended which will provide some relief.
When to contact a doctor:
Seek an advice from a gynecologist if one notices any discomfort, redness, itching, or swelling of the vulval area.
Prevention:
Maintaining a good vaginal hygiene and safe sexual practice is necessary. During active infection, unprotected sexual activity should be avoided. Use of mild soaps for cleaning the vulval area and proper drying should be done. The area must be cleaned from front to back. Moist innerwear should be changed after exercise or swimming. Use of irritating agents and douching at vaginal region must be avoided. Use of acidophilus supplement, intake of garlic, avoiding intake of alcohol, refined foods are the measures which need to be implemented in diet.
System Involved: Female genitals
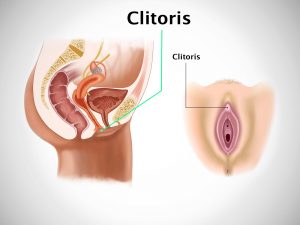
Organ involved: Vulva, vagina, labia majora, labia minora