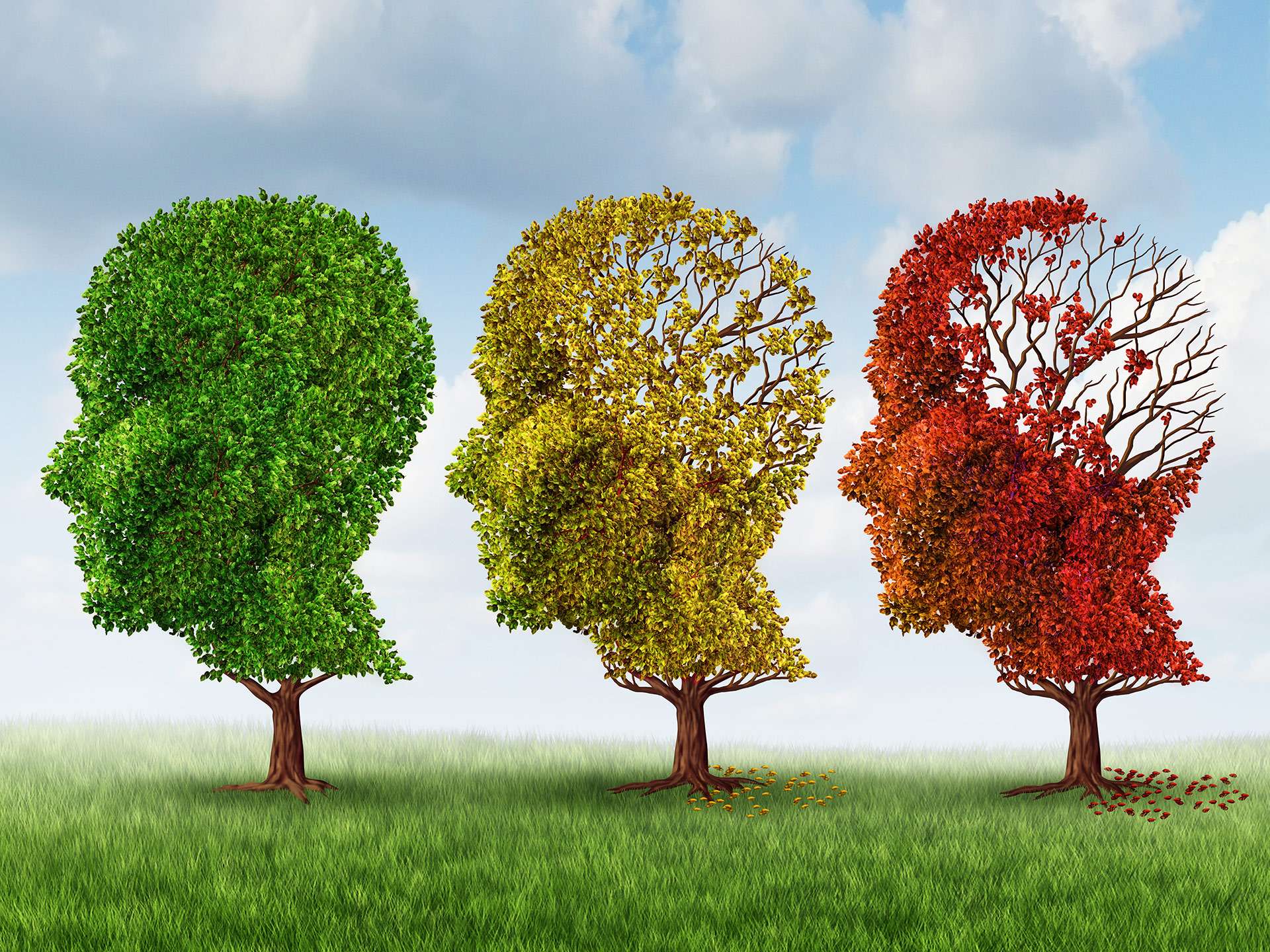
She had always been an incredibly charismatic woman. Therefore, it was extremely disturbing to see her in distress. Though it did not affect her daily activities, it was clearly evident that she was gradually forgetting things, misplacing them, losing track and sense of a conversation or sometimes even forgetting places and people – something which she had never done before. She was losing her memory, speech and her thinking abilities. She was becoming more impulsive and anxious.
Slowly, the ones around her began writing and sticking small notes all over the house – on the fridge, dining table etc. to keep her reminded. A clinical diagnosis revealed she was suffering from ‘Cognitive Impairment,’ often referred to as ‘Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI).’ It turned out to be well beyond the normal aging process, often considered an antecedent to depression, dementia or even Alzheimer’s. The medical practitioner explained that MCI often reflects mild but noticeable changes in the behaviour of a person, difficulties in multitasking and memory loss. It affects 10-20% of people above the age of 65.
Symptoms of cognitive impairment:
Cognitive impairment may be congenital or it may afflict at any point of a person’s lifetime.
Depression, anxiety, poor judgement, aggression, loss of reasoning, inability to focus, learning disabilities are some of the symptoms of Cognitive impairment.
Sometimes, along with the above symptoms, one may also face infection related problems like fever, headache, nausea, rashes, seizures.
Metabolic disorders may also accompany the above symptoms, such as, fatigue, frequent urination, abdominal pain, feeling thirsty often, slow or rapid heart rate.
Causes of cognitive impairment:
Chromosomal and genetic abnormalities, poor growth of the foetus, and exposure of alcohol or drugs to the foetus can lead to cognitive impairment being congenital.
Problems during delivery like infection, premature birth or lack of oxygen during birth can cause a new-born to be cognitively impaired.
Causes of cognitive impairment after birth can be many and sometimes no single cause can be determined.
- Ageing and a careless lifestyle (lack of exercise).
- Ailments such as diabetes, high blood pressure, thyroid or high cholesterol.
- Brain injury or strokes
- Growth in brain’s ventricles or plaques in the brain.
- Family history such as Alzheimer’s
- Malnutrition
- alcohol/drug abuse,
- vitamin deficiencies etc.
Treatment of cognitive impairment:
Treatment of Cognitive Impairment is currently an area of active research and as such there are no medicines that are approved by the Food and Drug Administration. Research is under way to throw more light on the subject and to find treatments to improve the condition.
Drugs that are used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease are sometimes prescribed for treating cognitive impairment but there has been no recorded history of successful recovery.
It has been observed that treating other conditions that commonly make a person seem mentally less capable can help improve the condition of cognitive impairment.
For instance, treating conditions like depression, insomnia, high blood pressure can facilitate improved memory and mental power.
On the whole, living a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, moderate consumption of alcohol, refraining from drugs and smoking, keeping yourself mentally active, meeting new people and engaging in social conversations will promote good health and keep one mentally fit.
Cognitive impairment is not a disease per se but a condition caused by various factors. Dealing with it becomes easier if one is aware of the causes, symptoms and the right steps to be taken to deal with it. In this condition, not only is the patient affected but also his or her family and friends. Likewise it needs the support and understanding of family and friends to cope with the impairment and mitigate its effects.
Cognitive impairment is becoming more rampant now but fortunately we are armed with the information, technology and means to deal with such impairment effectively.