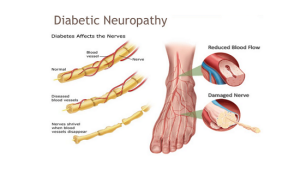
High blood glucose levels may lead to:
- Organ damage involving the kidneys (diabetic nephropathy)
- Nervous system (diabetic neuropathy)
- Eyes (diabetic retinopathy)
- Circulatory system
About obesity:
Obesity is a state of excess body fat. The prevalence of obesity is expressed by using body mass index (BMI), a simple index of weight-for-height that classifies underweight, overweight and obesity in adults. Excess weight and obesity lead to adverse metabolic effects on blood pressure, lipid levels and insulin resistance and thus pose a major risk for serious chronic diseases, including hypertension, Type 2 Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. In addition, obesity increases the risk of respiratory difficulties, chronic musculoskeletal problems, infertility, gallbladder disease, and certain forms of cancer.
Diabetes and Obesity:
Obesity is a major modifiable risk factor for one type of diabetes (Type 2 Diabetes).
The steps taken to manage diabetes and obesity must encourage and facilitate physical activity and a healthy diet, and control access to energy dense foods and drinks. Health promotion, particularly in relation to diet, weight control and physical activity, can play a part but it is not sufficient on its own.
Obesity, mainly the abdominal obesity, is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes and also for other non-communicable diseases such as heart attack and stroke. If weight gain is prevented most of diabetes cases can be eliminated.