Causes and risk factors
Abnormal posturing most often occurs due to damage to the brain or spinal cord. The area of the brain or spinal cord affected will decide the type of posturing one can experience. The causes are cerebral edema – fluid buildup in the skull and swelling of the brain, increased intracranial pressure due to SOL, intracranial hemorrhage, Reye syndrome, severe head injury, stroke, uncal herniation, meningitis, encephalopathy, brain tumor. Torticollis is also one of the forms of abnormal postures.
Clinical presentation
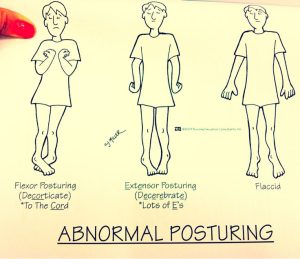
Abnormal posturing results when one muscle contracts and the other muscle fails to offer resistance. This causes atypical movement such as stiffness/arching of feet, hands, head, or back. There are three main types of postures shown among individuals with abnormal posturing. Opisthotonos is a posture in which the neck is tilted back and the back is stiff and arched. Decorticate posture is characterized by a stiff body, straight legs, bent arms held toward the chest, and clenched fists. Decerebrate posture is characterized by stiff, straight limbs, pointed toes, and a backward tilt to the head and neck.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Cerebral angiography is recommended. EEG is done. Head CT scan, head MRI scan, head x-ray are required. ICP monitoring is advised (intracranial pressure).
Treatment
Emergency care is required. It usually begins with placement of an artificial airway (breathing tube) and assistance with breathing. Further treatment is given after confirming the cause.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating abnormal posturing. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the Ayurvedic system of medicine, which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates, is also found to be effective in treating abnormal posturing.