Causes and risk factors
Exceptionally heavy bleeding during periods is termed as menorrhagia or hypermenorrhea, while light bleeding is called hypomenorrhea. If bleeding occurs between periods, this is not necessarily pathological, but it is termed as intermenstrual bleeding. Different causes responsible for abnormal bleeding per vagina are as follows:
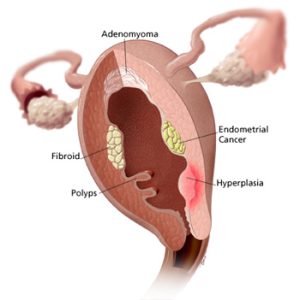
Bleeding in children – precocious puberty (early puberty), presence of a foreign body in the vagina, molestation, vaginal infection, and tumor. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is a common cause of abnormal bleeding per vagina. Additional causes include mechanical causes such as IUD, hormonal imbalance, polycystic ovary syndrome, uterine fibroids. Cervical cancer may occur at premenopausal age and often causes bleeding after sex. Uterine cancer will lead to irregular and often prolonged bleeding. In pregnant women, mild-to-moderate bleeding may be due to rupture of small veins on the outer rim of the placenta. It can also be a predisposing factor for a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. In the second or third trimester a placenta previa (a placenta partially or completely overlying the cervix) may bleed severely. Placental abruption is often associated with uterine bleeding as well as uterine pain. In a recently pregnant woman who has delivered a baby or who had a miscarriage, bleeding occurs. Retained products of conception can also cause vaginal bleeding. Vaginal bleeding may be a sign of endometritis. In postmenopausal women, uterine or vaginal bleeding can be due to unopposed estrogen, atrophic endometritis/vaginitis, endometrial cancer, endometrial polyps or cervical polyps, or endometrial hyperplasia.
Clinical presentation
Symptoms produced are variable depending upon the cause of the abnormal bleeding. Abnormal vaginal or uterine bleeding includes irregular periods, shorter menstrual cycles bleeding between 2 periods, prolonged menses, systemic symptoms such as anemia, weakness, pallor, weight loss, etc.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Routine hemogram is advised. USG of abdomen and pelvis is recommended. Endometrial biopsy, hysteroscopy, sonohysterography, laparoscopy may be required.
Treatment
Treatment for abnormal bleeding depends on several factors, including the cause, age, severity of the bleeding, and whether the patient is willing to conceive. Medical treatment includes birth control pills or hormones; anti-inflammatory drugs such as NSAID’s, antibiotics in case of infection. Change in contraception method is required if the cause is IUD. Anti-bleeding agents will help in managing bleeding which is not hormonal and will contribute further to the treatment. Surgery to remove polyps/fibroids/cancer; endometrial ablation; hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be required in severe cases.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating abnormal vaginal or uterine bleeding. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the Ayurvedic system of medicine, which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates, is also found to be effective in treating abnormal vaginal or uterine bleeding.





![Lobular Carcinoma In Situ [LCIS]](https://moho.loopshell.com/read/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Lobular-Carcinoma-In-Situ-Lcis-300x300.png)