Causes and risk factors
Causes include close shaving of the neck – the sharp, curved hairs reenter the skin and invoke an acute inflammatory response. Constant irritation from shirt collars or athletic gear, this irritation causes shearing of the hairs. Chronic low-grade bacterial infections can also cause this disease. It may be a form of an autoimmune process. It may develop after use of antiepileptic drugs. An increased number of mast cells in the occipital region can lead to this condition.
Clinical presentation
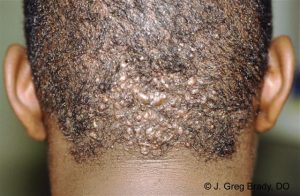
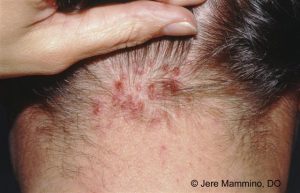
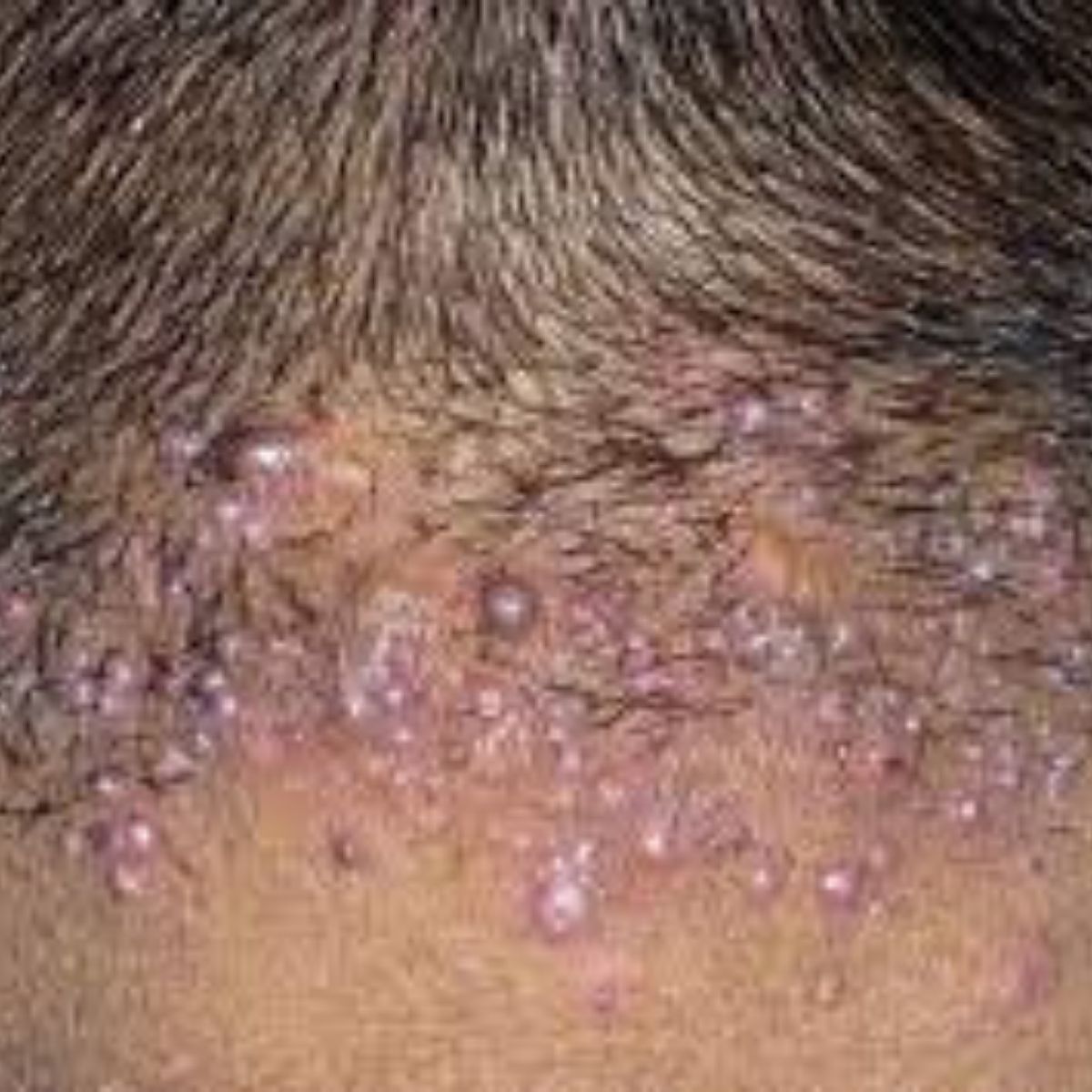
Lesions initially manifest as mildly pruritic follicular-based papules and pustules. Early lesions manifest as firm, dome-shaped that are 2-4 mm in diameter. The predominant location is on the occipital region and nape of the neck. Pustules may be present. The lesion causes itching. As the disease progresses, more papules and pustules appear and can eventually coalesce to form larger plaques. Chronic folliculitis leads to development of keloid-like plaques. Finally, keloid like plaques arranged in a band-like distribution at or below the posterior part of the hairline can be identified. The plaques are usually only a few centimeters in diameter, but they can be greater than 10 cm in diameter. Eventually, there is scarring alopecia. In chronic lesions, broken or tufted (“doll-like”) hair may be seen within or at the periphery of the plaque. Abscesses with draining sinuses may be present. Purulent discharge may occur. AKN develops in hair bearing skin areas, and broken hair shafts, tufted hairs, and ingrown hairs can be identified within and at the margins of the plaques themselves. Lesions can grow over time and become disfiguring and painful.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the dermatologist helps in diagnosis. Bacterial culture and sensitivity is done. Routine blood test may be advised. Skin biopsy is required.
Treatment
Topical and oral antibiotics, oral corticosteroids, intralesional steroidal injection are useful. Electrodessication, cryotherapy, radiation therapy will help in managing acne keloidalis nuchae.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating acne keloidalis nuchae. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the Ayurvedic system of medicine, which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates, is also found to be effective in treating acne keloidalis nuchae.