Causes and risk factors
The fibrous joints between bones of the skull (sutures) close prematurely, causing the condition. It can also be a hereditary condition. Genetic mutation can also lead to acrocephalosyndactyly. The best known type of acrocephalosyndactyly is Apert syndrome which is caused by mutations in F2G2 gene on chromosome number 10.
Clinical presentation
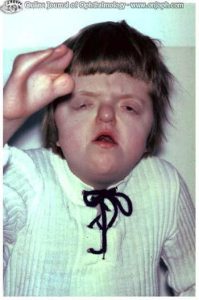
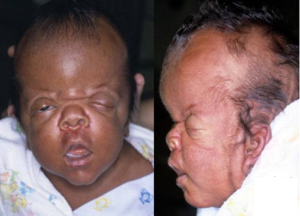
Too early closures of sutures result in abnormal formation of skull (craniosynostosis) characterized by tall, peaked head. Head abnormally pointed to the top. The skull is deformed and changed to other characteristic shapes. There is change in facial bones. Facial abnormalities such as wide eyes, protruding eyes is seen. Shallow eyes, sockets and underdeveloped mid face is seen. There is fusion of fingers and toes (syndactyly) with broad ends of thumbs and big toes. Malformation of hands or legs like webbed fingers, fusion of bones from second digit to fourth digit with a common nail is observed.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Ultrasound screening, x-ray, CT scan is recommended.
Treatment
Treatment varies depending on the type and severity of the deformity. Symptomatic and supportive treatment in mild cases is required. Physiotherapy will also help in managing the condition. Surgical correction of deformity may be required.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating acrocephalosyndactyly. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the Ayurvedic system of medicine, which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates, is also found to be effective in treating acrocephalosyndactyly.