Causes and risk factors
Causes of obstructive uropathy include enlarged prostate, bladder cancer, kidney stones, prostate cancer, cervical cancer, etc. Ureteropelvic junction obstruction, spasm of ureters, ureteric obstruction due to calculi, pelvic tumors, or metastatic lesions pressing on ureters are some of the causes. Surgical complication can cause the disease. Injury can lead to obstructive uropathy. Pregnancy may cause the disease. Blood clots, neurogenic bladder, posterior ureteric valves in infant boys can cause the disorder.
Clinical presentation
Patient presents with symptoms like leakage of urine, nausea and vomiting, need to urinate at night. There can be sudden flank pain or pain on both sides. There is difficulty in urination. There is abnormal color of urine. Patient complains of decreased urine output. There is feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, but a frequent strong urge to urinate. Abnormal urine flow -dribbling at the end of urination is observed. Blood in the urine is seen. Burning or stinging with urination is experienced by the patient. Accompanying symptoms include fever, increase in blood pressure, etc. Untreated acute bilateral obstructive uropathy leads to hydronephrosis and severe kidney damage.
Investigation
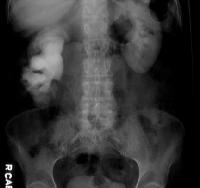
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Blood test is done. Ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys is recommended. IVP is recommended. Renal scan is advised. Abdominal CT scan may be required. Uroflowmetry, urodynamic studies are done.
Treatment
Treatment depends upon the underlying cause. Treatment includes administration of antibiotics. Catheterization may be needed. Drainage by putting ureteric stents is helpful. Surgery, i.e., transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) may be required. Laser therapy to shrink the prostate may be useful.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating acute bilateral obstructive uropathy. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly, the Ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates, is also found to be effective in treating acute bilateral obstructive uropathy.