Causes and risk factors
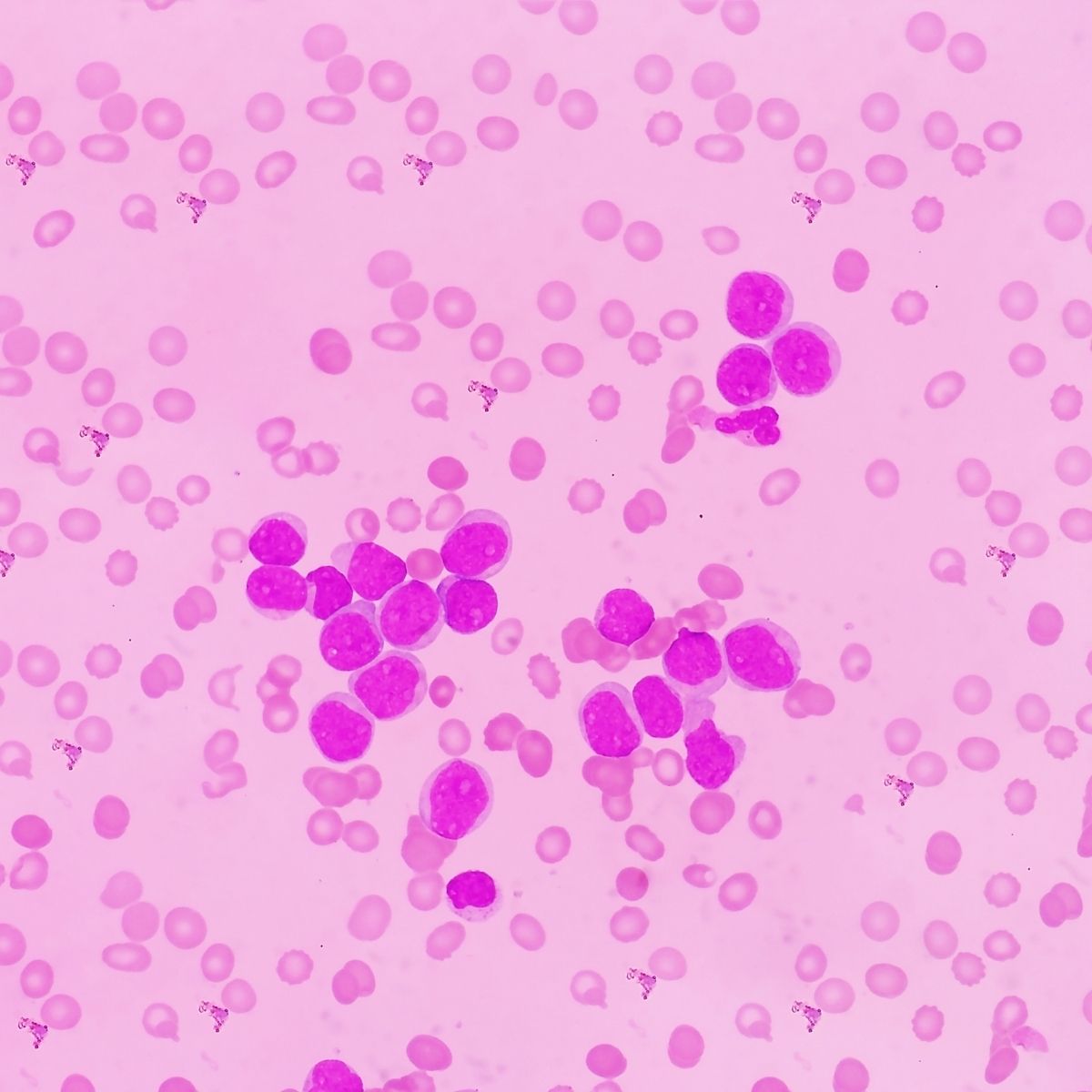
Exact cause of ALL is not known but it is caused due to mutations in the DNA. Errors in DNA cause cell to continue to divide and multiply. This leads to accumulation of immature cells in the bone marrow. The risk factors for ALL are previous history of treatment for cancer, exposure to radiation, genetic disorders like Down’s syndrome or kleinfilter’s syndrome or siblings with ALL. Risk of getting ALL is higher in males than in females.
Clinical presentation
ALL presents as Bleeding from gums, bone pain, fever, frequent infections, epistaxis, enlarged lymph nodes around neck, underarms, abdomen, pallor, shortness of breath, generalised weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite and weight loss.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Tests include Routine haemogram, bone marrow biopsy, lymph node biopsy, lumbar puncture. A PCR test can identify ALL cells based on their gene translocations. Imaging such as X ray, CT and MRI will help to diagnose whether there is invasion of other organs of the body.
Treatment
The earlier the diagnosis more effective will be the treatment. Initial treatment includes chemotherapy which consists of 3 phases – remission induction, consolidation, and maintenance therapy; radiation therapy, targeted drug therapy, stem cell transplant and bone marrow transplant are found to be effective in treating ALL.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating ALL. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating ALL.
Facts and figures
ALL is the commonest type of childhood cancer accounting 25% of all cancers in children. Children below 5 years of age at are high risk.