Causes and risk factors
Albinism is a genetically inherited disorder. There is defect in the genes which are responsible for producing melanin pigment which gives colour to the skin and hair. These genes are inherited from both the parents. Inheritance pattern is as follows – if one of the parents is affected and other is unaffected, there are 50 % chances of child being affected and 50 % of it being normal. If both the parents are carrier, there are 25% chances of child being affected, 25 % chances of it being normal and 50% chances of the child being a carrier. If one of the parents is normal and the other is carrier, there are 25 % chances of the child being affected, 25% of it being affected, and 50% chances of being normal.
Clinical presentation
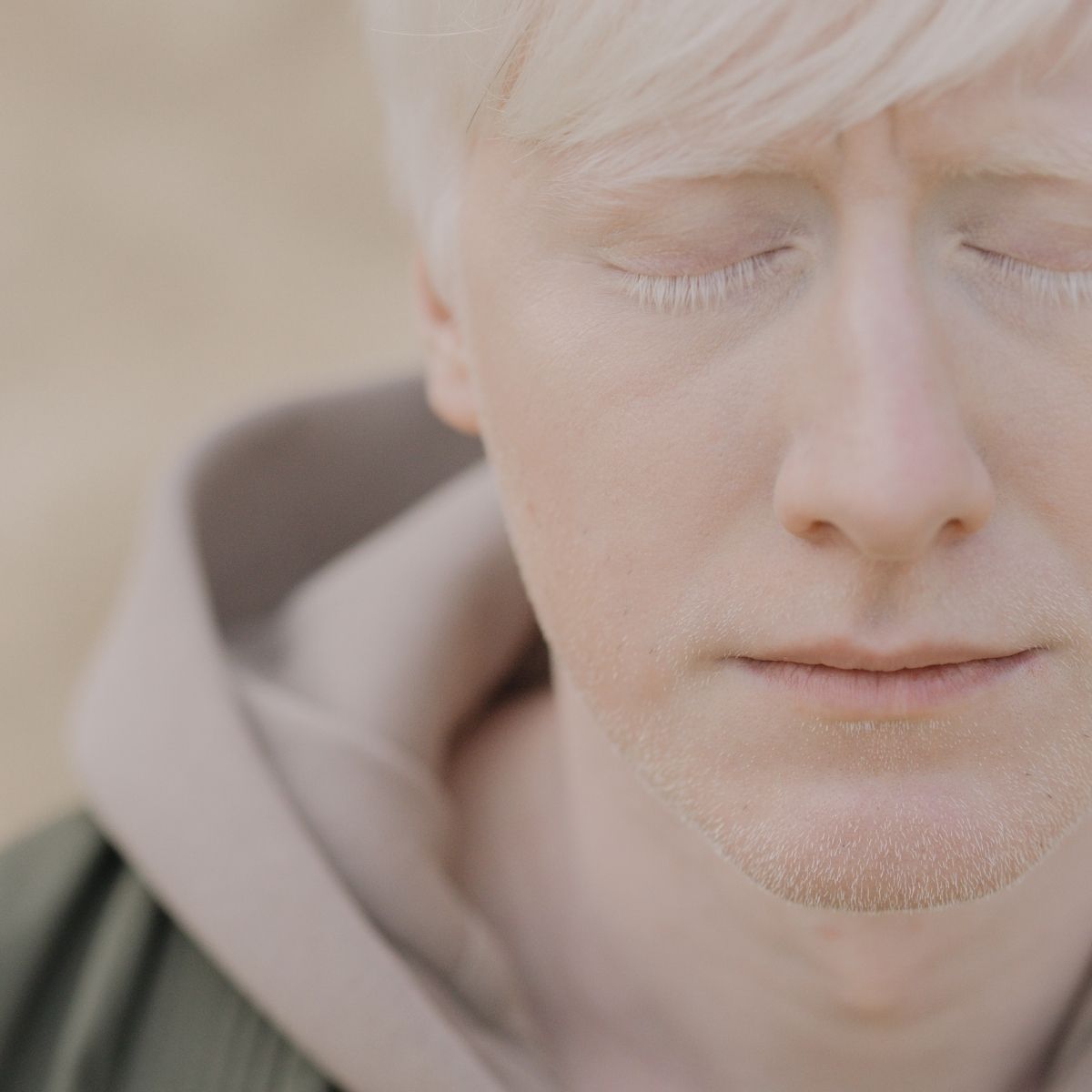
Albino patient presents with signs and symptoms like absence of colour in the hair, skin, or eyes. The colouring of the hair, skin, or eyes is lighter than normal. There are patches on the skin that have an absence of colour. Patient complains of photophobia, involuntary rapid eye movements [nystagmus], strabismus and impaired vision or refractory errors. Albinism is classified as occulocutaneous [OCA] which involves eyes, skin and hair; and only ocular albinism [OA] which involves only eyes while the skin and hair appear slightly lighter than normal. Types of OCA and their features are as follows. OCA type 1 results into white hair and light skin. It is caused due to deficiency of enzyme called tyrosinase responsible for production of melanin. It has further subtypes OCA type 1A and type 2A. OCA type 2 in caused due to defect in P protein. It results in hair colour ranging from light blond to brown. OCA type 3 is caused as a result of defect in protein. TYRP1 while OCA type 4 is caused due to defect in the protein SLC45A2. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome is another type of albinism which involves bleeding and bruising along with whitening of skin and hair. Lung and bowel disease are also accompanied.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the dermatologist helps in diagnosis. Eye examination is recommended. Genetic testing confirms the diagnosis.
Treatment
There is no cure for albinism. Protective treatment like wearing sunglasses, wearing protective clothes while going out like sun coats, gloves, use of sunscreen lotions will help in managing albinism. In ocular albinism eye surgery may be required to correct strabismus.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating albinism. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating albinism.
Facts and figures
Albinism occurs in 1 in 3000 individuals all over the world.