Causes and risk factors
The exact cause of development of Alzheimer’s disease is still not understood clearly.
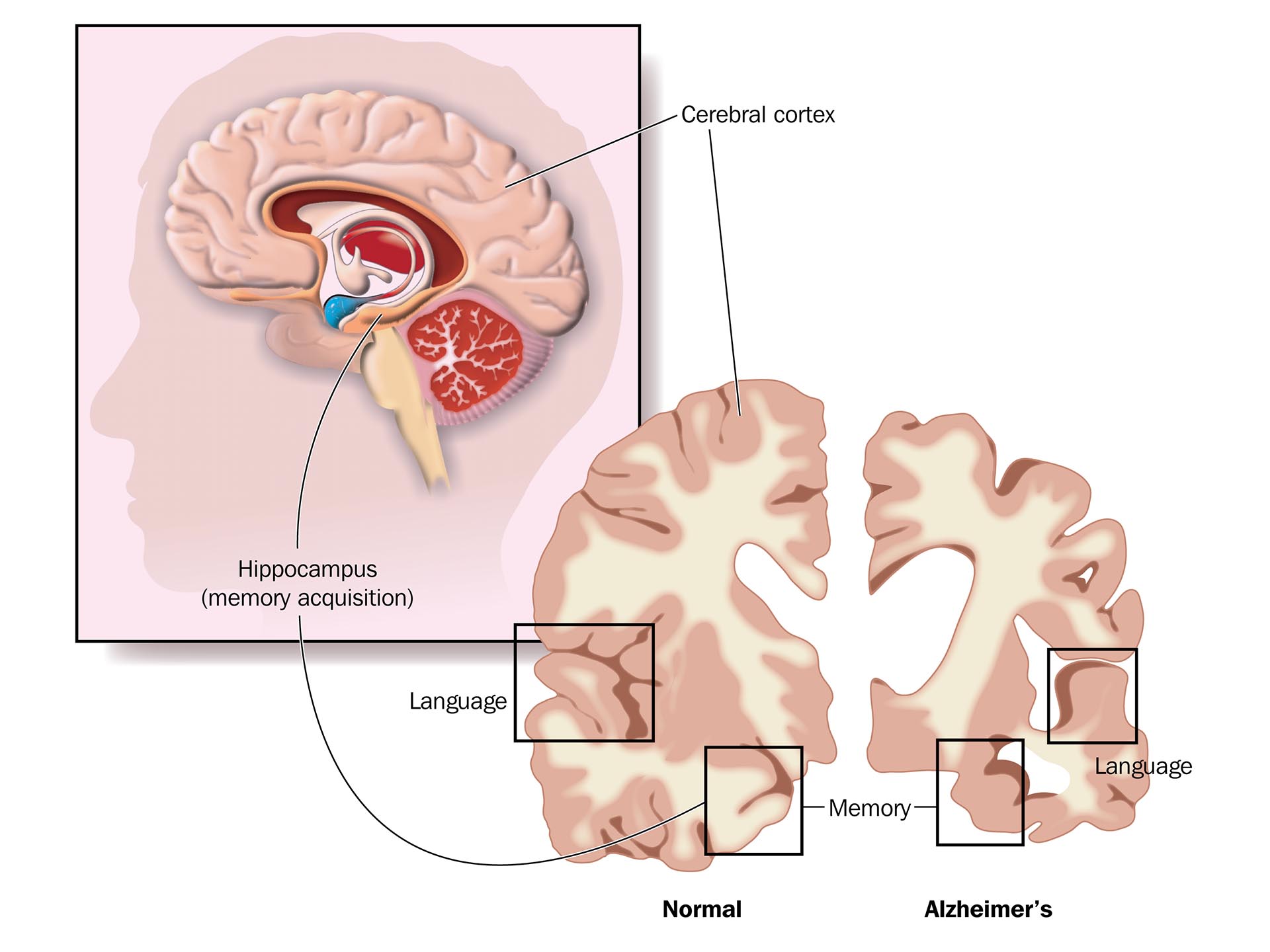
Most scientists believe it involves complex mix of genetic, environmental and lifestyle factors. Accumulation of protein amyloid plaques, tangles in the brain and the loss of connections between nerve cells [neuron] in the brain are the main features of the Alzheimer’s disease.Risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease include family history, longstanding high blood pressure, history of head trauma, high levels of homocysteine [a body chemical that contributes to chronic illnesses such as heart disease, depression, and possibly AD], and female gender. It maybe accompanied with other psychiatric disorders like dementia, depression etc.
Clinical presentation
Memory loss or memory lapses is the first sign of Alzheimer’s disease which is often mistaken by family members as normal part of aging.Memory loss is usually seen for recent events. Signs and symptoms like difficulty in performing day to day task, struggling to follow a conversation, repeating statements, misplacing items, having trouble finding names for familiar objects, getting lost on familiar routes are observed. Personality changes like tendency to withdraw from social interactions, difficulty performing tasks that take some thought, but used to come easily, like balancing a checkbook, playing complex games [such as bridge], and learning new information or routines. In a more advanced stage, problems with memory loss, orientation, reasoning and communication become more severe. Symptoms are more obvious like forgetting details about current events, forgetting events in your own life history, losing awareness of who you are, problems choosing proper clothing, hallucinations, arguments, striking out, and violent behavior, delusions, depression, agitation, difficulty performing basic tasks like preparing meals and driving. At end stages of AD, a person can no longer survive without assistance. Most people in this stage no longer understand language, recognize family members, perform basic activities of daily living such as eating, dressing, and bathing etc.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the psychiatrist or psychologist helps in diagnosis. Routine blood tests are recommended. Imaging studies such as CT scan and MRI may be useful for further evaluation. Neuroimaging, neuropsychological testing is advised.
Treatment
There is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease. But treatments options are available that can temporarily slow the progression of dementia symptoms and improve the quality of life of the patient and their care givers.Treatment includes lifestyle changes, medications, and antioxidant supplements. Lifestyle changes such as walking regularly with a caregiver or other reliable companion. This can improve communication skills and prevent wandering.Using bright light therapy to reduce insomnia and wandering.Listening to calm music may reduce wandering and restlessness, boosts brain chemicals, eases anxiety, enhance sleep, and improve behavior.Getting a pet dog.Practicing relaxation techniques. Several drugs are available to try to slow the progression of AD and possibly improve the person’s mental capabilities. Certain supplements are said to have some role in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease:
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating Alzheimer’s disease.Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating Alzheimer’s disease.
Facts and figures
There is 1 in 6 women developing Alzheimer’s disease around 60 years of age. A person with Alzheimer’s lives for around 8-10 years since the beginning of disease. More than 500000 seniors die every year due to Alzheimer’s.