Causes and risk factors
Most cases of amblyopia occur in the first few years of life before the age of six.
Deprivation amblyopia: Congenital cataract is a common cause of deprivation amblyopia. Opacities of the cornea or vitreous and ptosis (drooping of eyelids) are other known causes.
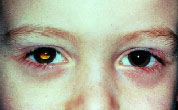
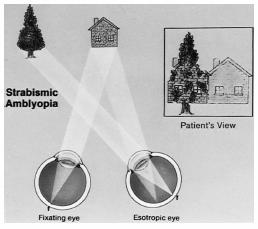
Strabismic amblyopia: This form of amblyopia is caused as a result of strabismus in one or both the eyes. Strabismus is a misalignment of eyes: Upwards, downwards, inwards, or outwards.
Refractive amblyopia: An unequal refractive error in both the eyes (anisometropia) gives rise to refractive amblyopia. Since the brain ignores the blurred images from the bad eye, only half the visual system develops normally, whereas the other half remains undeveloped.
Clinical presentation
The visual acuity of the child is reduced to a variable extent. The perception of depth is hampered and hence, three-dimensional vision is difficult. Their spatial acuity (ability to detect shapes) and contrast sensitivity (detection of contrast between an object and its background) is poor. Their vision is less sensitive to motion and they frequently experience crowding phenomenon. Their stereoscopic ability (3 dimensional vision) is impaired and they are unable to carry out binocular summation (combining the information received from both the eyes). Children with strabismic amblyopia have a reduced reading speed and their eyes move abnormally while reading.
Investigations
Amblyopia can be detected by an ophthalmoscopic examination.
Treatment
The underlying cause of amblyopia needs to be treated.
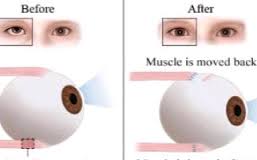
Surgery is usually recommended for congenital cataract and strabismus.
Corrective contact lenses are the preferred mode of treatment; however, corrective glasses may also be used. Refractive surgery can also be considered.
Patching of the good eye helps to improve the vision in the other eye. A procedure known as penalization is also recommended, wherein atropine drops are put in the good eye in order to blur its vision. This helps to develop the visual acuity of the other eye.
Complications
Amblyopia can result in loss of visual acuity up to the extent of blindness.
When to contact a doctor
Contact a doctor if you suspect that you kid is having any visual trouble.
Systems involved
Ophthalmology.
Organs involved
Eyes.