Causes and risk factors
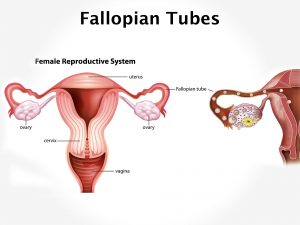
Exact cause of Amniotic fluid embolism is not known. It occurs if this fluid enters the maternal blood stream through the torn foetal membranes. It causes anaphylactic reaction leading to inflammation and clotting in the blood vessels. Contributing factors for AFE include advanced maternal age[ above 35], preeclampsia, placental abnormalities like placenta previa or abruptio placentae, C section, forceps or vacuum delivery, genetic cause
Clinical presentation
AFE is an obstetric emergency. Patient presents with chills, nausea, vomiting, sudden shortness of breath, low BP, tachycardia, arrhythmia, disseminated intravascular coagulation [DIC]. In advanced condition patient has altered sensorium, seizures, and coma. If not treated immediately patient goes into pulmonary oedema and congestive cardiac failure causing sudden cardiac arrest.
Investigation
Signs and symptoms of the mother or the baby and Clinical examination by the gynaecologist help in diagnosis.
Treatment
If AFE occurs after delivery it involves maternal monitoring. Treating maternal distress, Oxygen supplementation, measuring arterial blood pressure, insertion of central venous catheter for administration of fluids, medications for regulating BP, and blood transfusions in case of heavy blood loss will help in managing AFE. If it occurs before delivery, emergency C section is done and further treatment is given. Proper ventilator support and stabilisation is required.
Facts and figures
AFE is a rare complication. It occurs in 1 to 12 among 1, 00,000 deliveries.





![Lobular Carcinoma In Situ [LCIS]](https://moho.loopshell.com/read/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Lobular-Carcinoma-In-Situ-Lcis-300x300.png)