Causes and risk factors
Amoebic lung abscess is a type of abscess in the lung caused by an intestinal parasite, Entamoeba histolytica. When the amoeba enters mesenteric venules, they enter portal circulation and reach the liver. Extension of abscess occurs from liver to lungs. Transmission occurs through ingestion of cysts from fecally contaminated food or water. Flies and other arthropods also serve as mechanical vectors; transmission also results from contamination of food by the hands of food handlers. Where human excreta is used as fertilizer, it often becomes a source of food and water contamination. Person-to-person contact is also important in transmission of the disease; it can affect any one but the infection is more common in young and middle aged adults. Risk factors for severe amoebiasis include alcoholism, cancer, malnutrition, old age, pregnancy, recent travel to a tropical region, use of corticosteroid medication to suppress the immune system. Predisposing conditions for amoebiasis include crowding, poor sanitation, and poor nutrition.
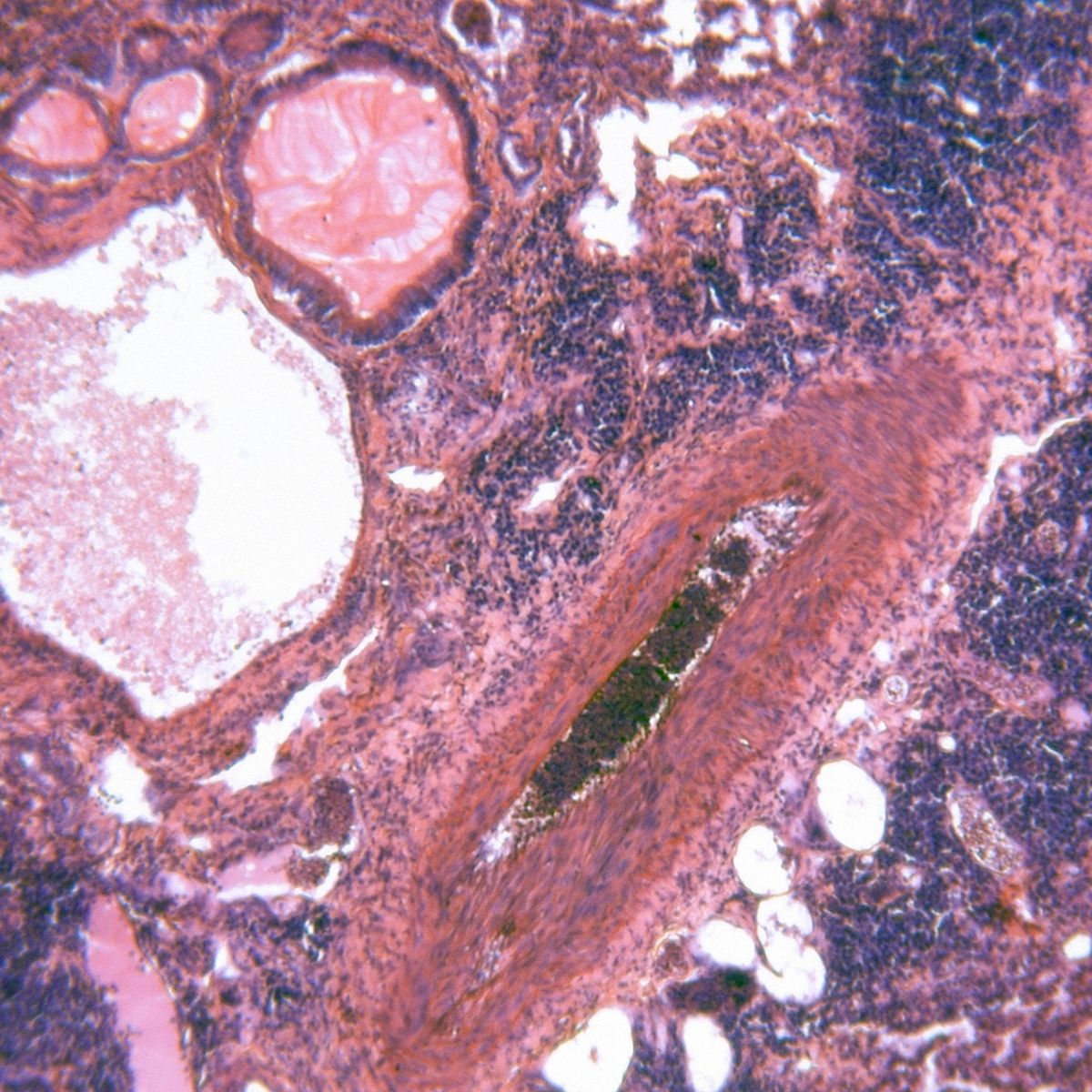
Amoebic lung abscess can be primary or secondary. Primary term indicates absence of amoebic liver abscess. The extension of infection occurs directly from intestine to the lungs by lymphatics or hematogenous spread. Secondary term indicates underlying amoebic liver abscess. The mode of spread to the lungs occur due to rupture of diaphragm. The abscess ruptures into pleural space or lungs. The spread can also be through adhesion between diaphragm and pleura. The amoebic abscess erodes the adhesions, giving rise to ‘collar stud’ or ‘collar button’ abscess in the lung. The condition commonly occurs in males.
Clinical presentation
Patient complains of pain in right lower chest or right shoulder. Right sided pleural effusion is the commonest sign. Dry cough with chocolate coloured sputum with haemoptysis is observed. Sputum may be greenish yellow and fowl smelling. Accompanying symptoms such as fever with chills, anorexia, weight loss, loss of appetite are observed. Signs such as fluid in the pleural space, tracheal shift, consolidation can be seen during examination.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Complete blood count is recommended. Chest x-ray is advised. Sputum culture, trans-tracheal aspiration is done. Bronchoscopy is done. Serology for amoebiasis confirms the diagnosis. Stool culture for identification of organism is needed. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound of the abdomen will reveal underlying amoebic liver abscess.
Treatment
Medicines include antibiotics, especially anti-parasitic, antiprotozoals; anti-spasmodic, NSAIDs. Probiotics may be tried to help the growth of healthy bacteria. Surgical intervention is needed to drain the abscess. Prevention is possible by washing hands thoroughly with soap and hot running water for at least 10 seconds after using the toilet or changing a baby’s diaper and before handling food. Cleaning bathrooms and toilets often, avoiding sharing towels or face washers, avoiding raw vegetables when in endemic areas, as they may have been fertilized using human faeces, boiling water, or treating it with iodine tablets.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating amoebic lung abscess. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the Ayurvedic system of medicine, which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates, is also found to be effective in treating amoebic lung abscess.