Causes and risk factors
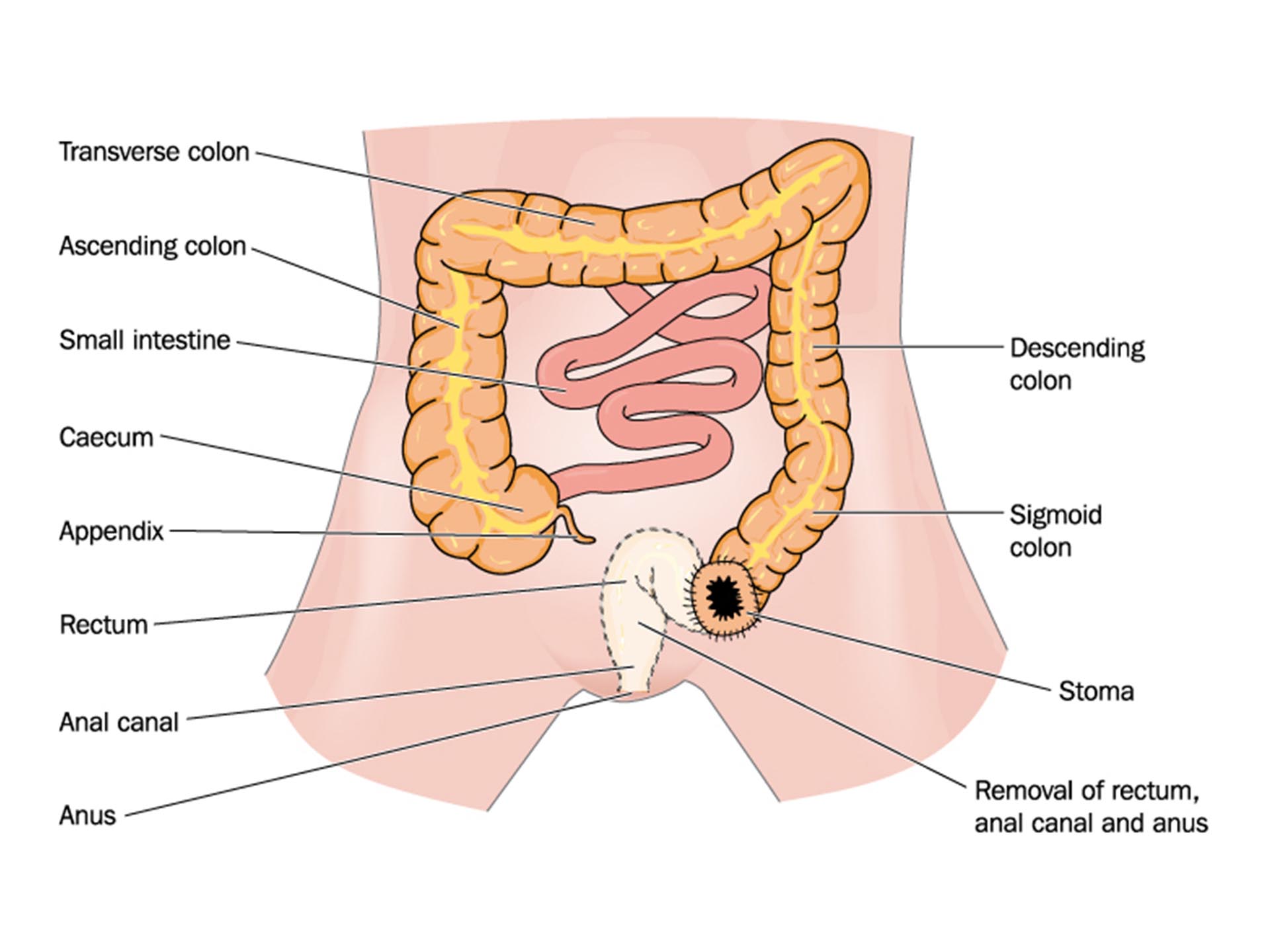
The exact cause of cancer is not known, but various risk factors or predisposing factors have been put forth. It is found that the cells undergo an uncontrolled and abnormal proliferation which gives rise to formation of tumors. Genetic predisposition is one of the major causes. People with weak immune system are more prone for cancer. Exposure to human papilloma virus poses high risk for developing anal cancers. Engaging in multiple sexual relationship increases the risk for HPV infection .Having anal fistulas, smoking cigarettes contribute to the causation. Anal cancer can be caused secondary to other cancers occurring in the body. It is more commonly seen in cervical and vulval cancers.
Clinical presentation:
Majority of the cases the patient remains asymptomatic in the initial phases. As the pathology advances various symptoms can be seen. The patient usually comes up with a complaint of pain and pressure in the pelvic region. Difficulty in passing stools occurs. On examination the anal region is red and soreness is seen. Itching in anal region and discharges along with bleeding from anus occur. Alteration in the bowel habits is complained by the patient. Weight loss, fatigue, loss of appetite is the other associated symptoms seen. Other symptoms pertaining to the system affected are also seen.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done on the basis of symptoms narrated by the patient and the examination carried out by the doctor. Per rectal vaginal examination is carried out by the doctor. Certain investigations like routine blood test, Blood markers for cancer Ultrasound scanning of the abdomen and pelvis and CT scans of abdomen and pelvis are firstly advised. On detection of any abnormalities anoscopy or proctoscopy is done. Later biopsy is recommended. A complete scan (PET scan) of the body along with other investigations can also be recommended for metastasis.
Treatment:
Depending upon the extend and stages of cancer the treatment is planned. Various surgical approaches can be adopted. Depending upon the extent of the cancer. Surgical intervention consist of removal of the cancerous tumor .Radiation therapy is used. Targeted chemotherapy and immunotherapy agents are administered.
Recent update:
A study conducted by the University of California has suggested that men ages 40-69 who are having sex with other men, are HIV-infected and smoke are at a much higher risk of HPVs that most often cause anal cancer.