Causes and risk factors
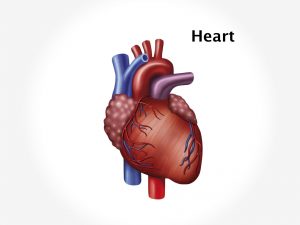
Heart muscle is working all the time, so it needs a continuous supply of oxygen. This oxygen is provided by the coronary arteries, which carry blood. When the heart muscle has to work harder, it needs more oxygen. Symptoms of angina occur when the coronary arteries fail to provide this excess blood demand. This condition seen in coronary artery disease. It is caused as a result of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a condition in which fatty material deposits along the walls of arteries. This fatty material thickens, hardens and form hard structures called plaques. Eventually, the plaques can make the artery narrow and less flexible, making it harder for blood to flow thus depriving heart muscle of oxygen rich blood supply. Deposition of plaques eventually leads to formation of thrombus or blood clot. If the clot dislodges and moves through the bloodstream, it can get stuck in the brain, lungs, heart, or other area, leading to obstruction, hampering the blood supply causing ischemia. The pain is caused due to spasm of the affected coronary artery, causing temporary narrowing of the artery and hampering blood flow to the heart. Angina pectoris or pain of stable angina is caused during exercise, climbing stairs, walking, in cold weather, emotional stress, after heavy meals. This pain is reduced by rest. Unstable angina – this pain is not reduced by rest. It is recurrent pain. Variant angina [prinzmetal’s angina] – pain occurs during rest and sleep. It is less common.
Clinical presentation
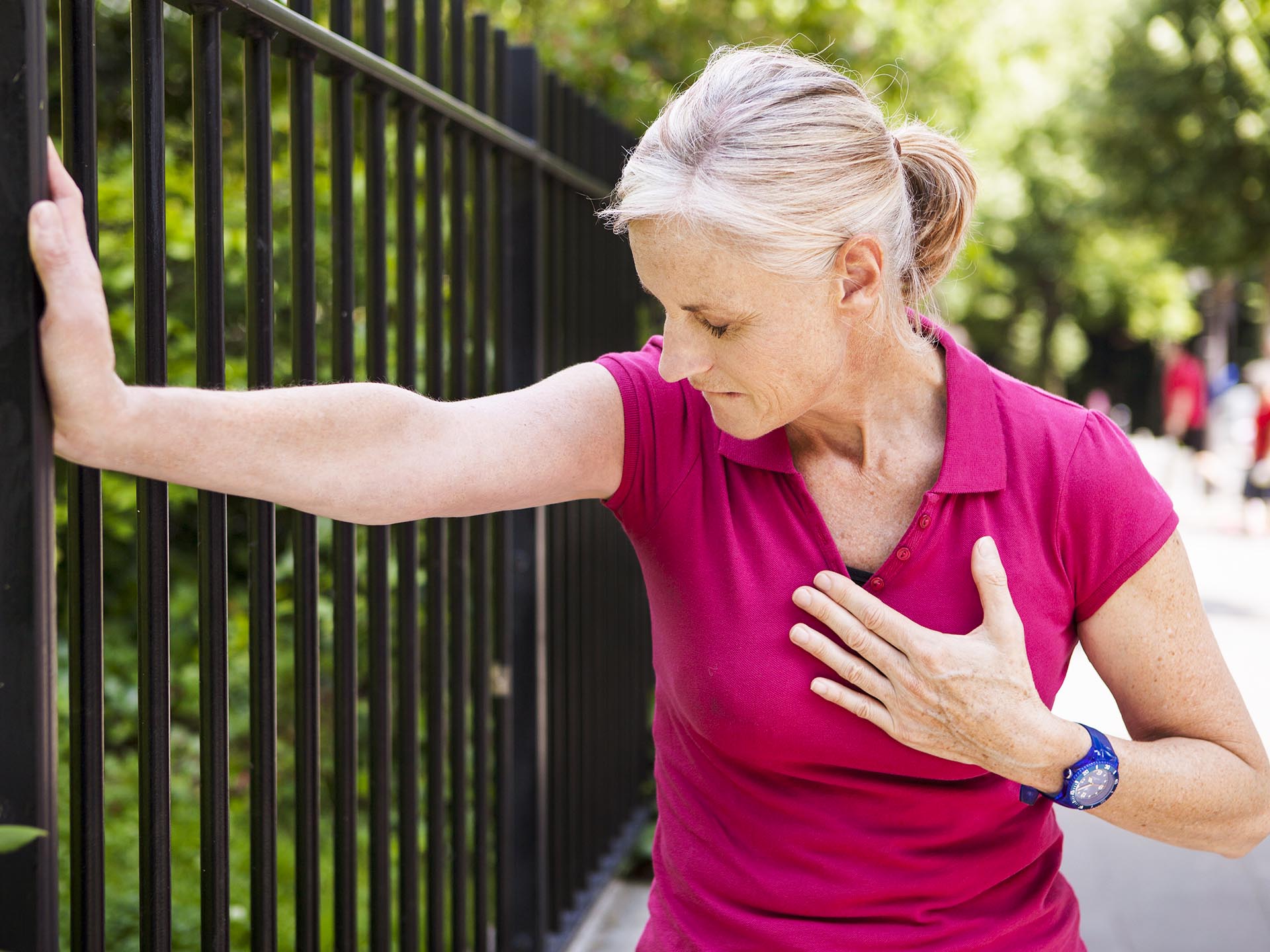
The patient presents with pain in chest. There is burning, pressure and tightness in chest. Pain is squeezing and crushing type. Pain which is referred to other parts example chin, jaw, left arm, stomach etc. There can be nausea, vomiting, difficulty in breathing. There is profuse sweating. Additional symptoms include dizziness, fatigue, and cold clammy skin, and restlessness, urgency to pass urine or stool. Angina pain can mimic musculoskeletal pain due to cervicospondylosis and many a times disguised as heartburn or pain due to GI reflux. Any chest pain should be thoroughly evaluated because it is warning sign of impending heart attack in high risk group patients.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. ECG is required. Routine blood test, Blood tests for cardiac markers is done. Pulse oximetry is done. Echocardiography, Stress tests is advised. Surgical procedures include Coronary angiography and cardiac catheterisation.
Treatment
Unstable stable angina or ACS is a medical emergency and requires immediate hospitalization. Stable angina pain is better by rest and avoiding any physical exertion or stress. Nitrates usually sublingual tablets are given which reduce the pain in case of stable angina. Blood thinning medicine, medicines to control blood pressure, anxiety, abnormal heart rhythms, and cholesterol are prescribed. Angioplasty is required if there is severe blockage or narrowing of the artery which is followed by stent placement to keep the artery open. Coronary artery bypass graft [CABG] is recommended in severe cases. Additionally your doctor may recommend lifestyle modification measures such as eating heart healthy diet, regular exercise, quit smoking, tobacco, alcohol and keep a check over blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol levels which contribute further to the treatment.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating angina. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating angina.