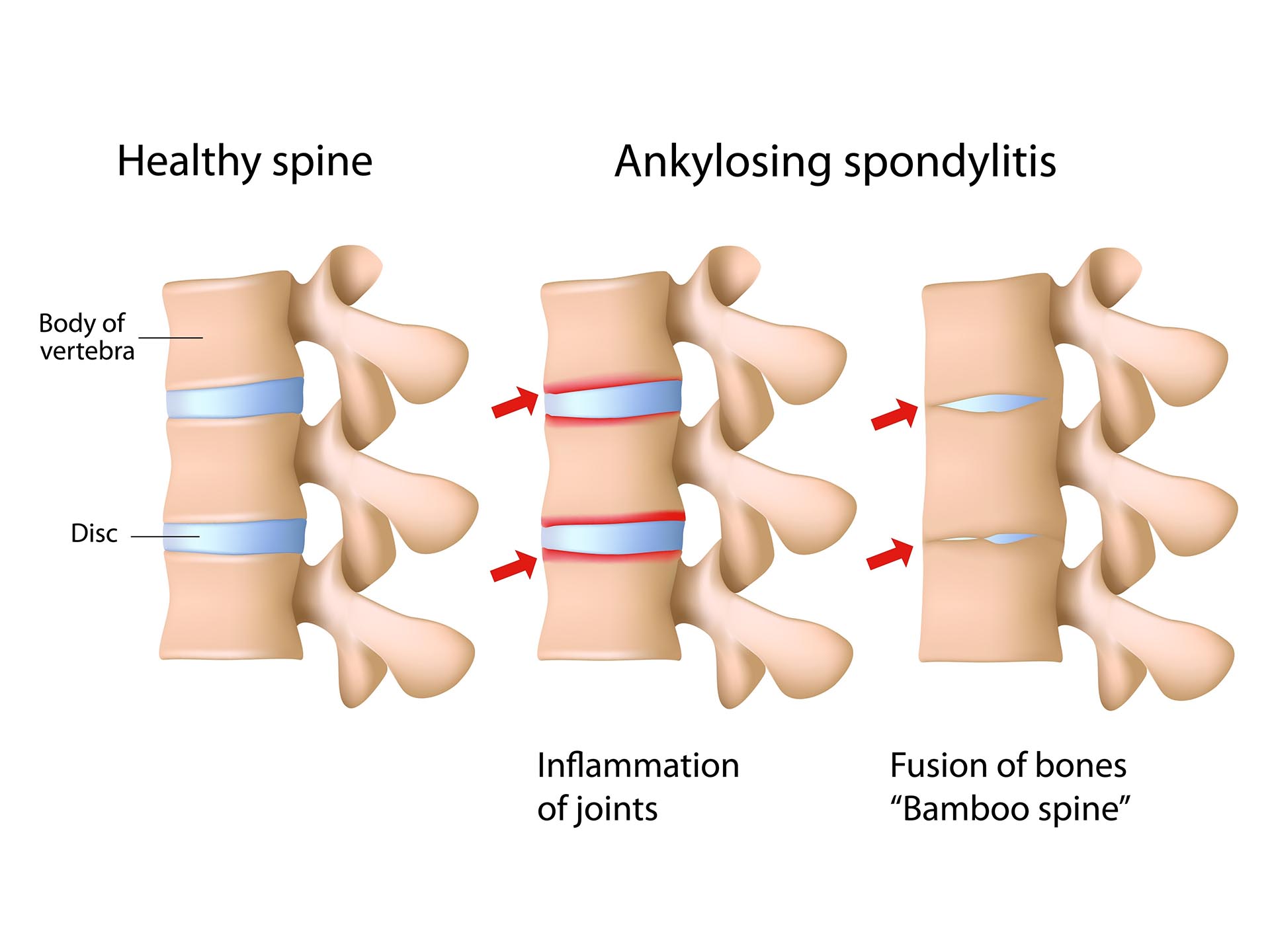
Causes and risk factors
The exact cause is not known. Genetic association is one of the major cause.HLA B27 is said to be one of involved genetic marker. There is a progressive inflammation(arthritis), degenerative changes in the vertebrae of spine which ultimately fuse together to cause stiffness and spinal mobility problem.Certain external triggering factors may also be responsible for provoking ankylosing spondylitis; however research is till going on in this field. Obesity can predispose pain in back and hip region.
Clinical presentation:
Symptoms develop gradually. Pain is the characteristic feature. It is accompanied by stiffness and loss of mobility. Pain is commonly seen in back and hip region. It is aggravated at night and early in the morning and is ameliorated by walking for a while, or after exercises. Pain may vary from person to person. The inflammation can also lead to involvement of other joint and bones of the body giving rise to variety of symptoms. The patient can also experience complaints like pain in joint, difficulty in movement, pain in neck region or in heel. It can also involve sternal bone leading to difficulty in breathing. Muscle weakness, malaise and tenderness are also present. In later stages deformities of the hip and back can occur (e.g.: kyphosis).
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done of the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the physical examination carried out by the doctor. Certain physical tests can be carried out by the doctor. X-ray of the spine is the diagnostic investigation.HLA B27 levels are elevated. As per the symptoms X-ray of the joints affected, MRI or CT scan can also be involved. Routine blood test and a profile of specialized blood test are other investigations which can be done to categories the type of arthritis.
Treatment:
The treatment aims at relieving the symptoms, the pathology cannot be reversed.
Change in lifestyles is necessary to correct the pain. Weight reduction in obese, adequate rest, correction of wrong postures needs to be adopted. Wearing of braces and back during movement, cold and hot compressions along with medications can be advised. Non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAID), steroids, DMARDS (Diseases modifying anti rheumatic drugs) and pain relieving drugs are prescribed. In severe cases corticosteroid injections and topical pain relieving gels and lubricants are advised. Patients who are not responding to medications and with underlying causes as degeneration of the knee joint etc are treated with surgical intervention. Physiotherapy exercises can help in improving the strengthen of the muscles and mobility of joints.
Other Modes of treatment:
Certain other modes of treatment can also be helpful in coping up the symptom. Taking into consideration the symptoms in holistic way, homoeopathy can offer a good aid for the relief of the symptoms. The Ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbs and synthetic derivates can also be beneficial in combating the complaints. Acupuncture which is the science of insertion of fine needles on the certain stimulating spots on the body has proved to be effective. Certain yoga exercises can also be helpful in relieving the pain and strengthening the muscles.