Causative & risk factors
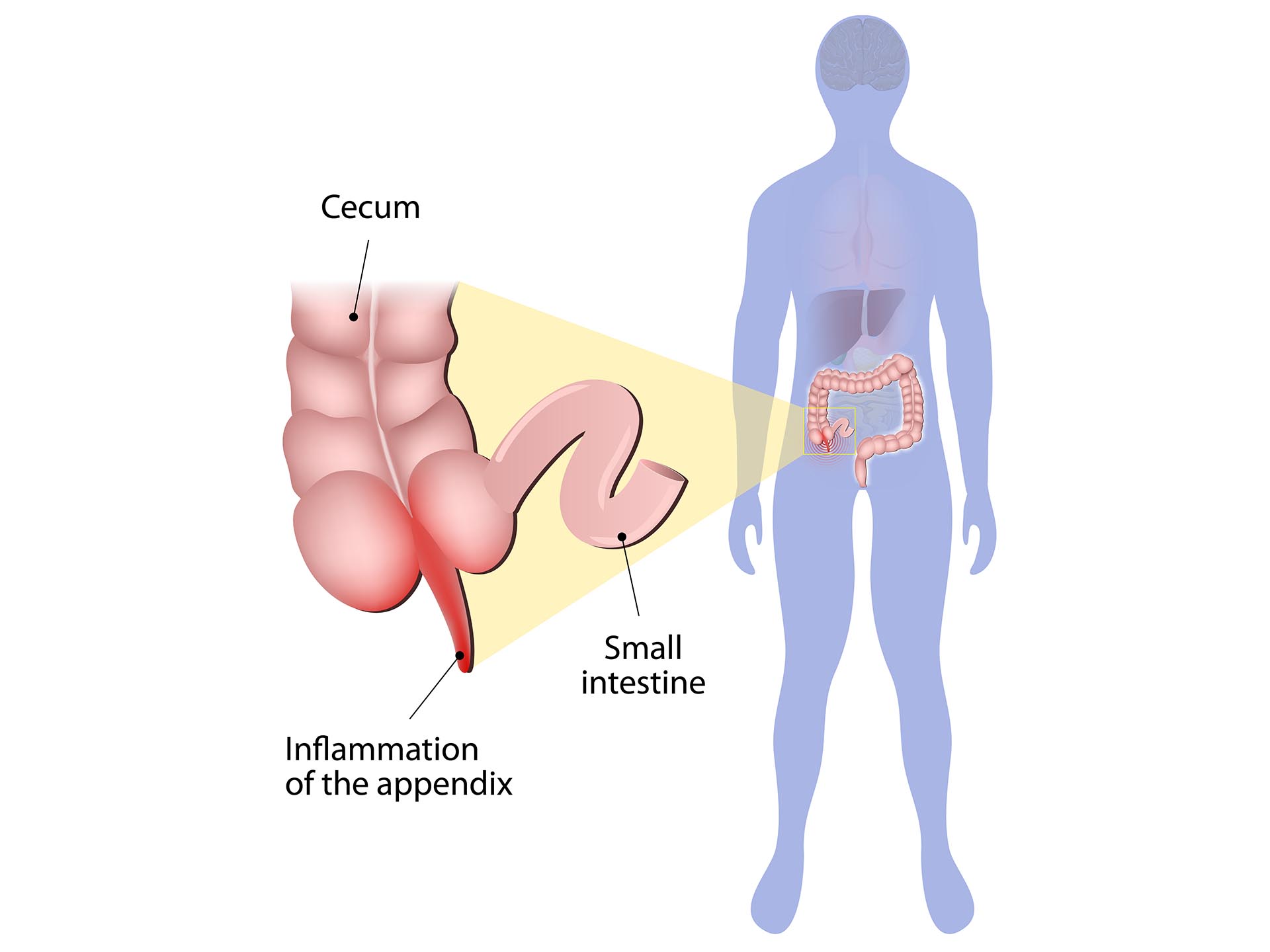
Any kind of blockage in the appendix can cause appendicitis. This may result due to stools, a foreign body or an infection.
Clinical presentation (with complications)
The typical clinical picture is that of a sudden, severe pain developing in the middle of the abdomen which then localizes just above the appendix i.e. in the right lower abdomen. Any kind of movement, even coughing can worsen the pain. Sometimes, pain may radiate to the epigastrium or back.
Abdominal pain is usually associated with nausea, vomiting, and fever. Constipation or diarrhea can also be present.
If the appendicitis is not treated on time, there is a risk that the appendix will rupture into the abdominal cavity. If this happens, the affected person will complain of severe pain all over the abdomen and his abdomen will become rigid (peritonitis). After bursting, there is also a possibility of abscess formation or abdominal sepsis.
While diagnosing appendicitis, one must consider the possibility of colitis, urinary tract infection, cholecystitis, pelvic inflammatory disease or other causes of pain in the abdomen.
Investigations
Appendicitis is diagnosed on the basis of the patient’s symptoms and physical exam of the abdomen by the doctor. Blood tests, urine tests and imaging tests (X-ray, ultrasound, CT scan) may be carried out to eliminate other causes of abdominal pain.
Treatment
Appendicitis is a medical emergency. Immediate surgery is necessary to remove the inflamed appendix. Appendectomy can be done as an open surgery or a laparoscopic procedure. Antibiotics are given prior to the surgery. Usually, the prognosis after appendix removal is good.
In children it is advised to subject them to a bedside ultrasound rather than CT scans and antibiotics are given. Surgery is avoided unless it’s a complicated case.
Recent updates (with references)
Nowadays doctors have started believing that it is better to treat patients of uncomplicated appendicitis with antibiotics first and try to avoid surgery. This helps to avoid the side-effects and prevent unnecessary surgery.