Causes and risk factors
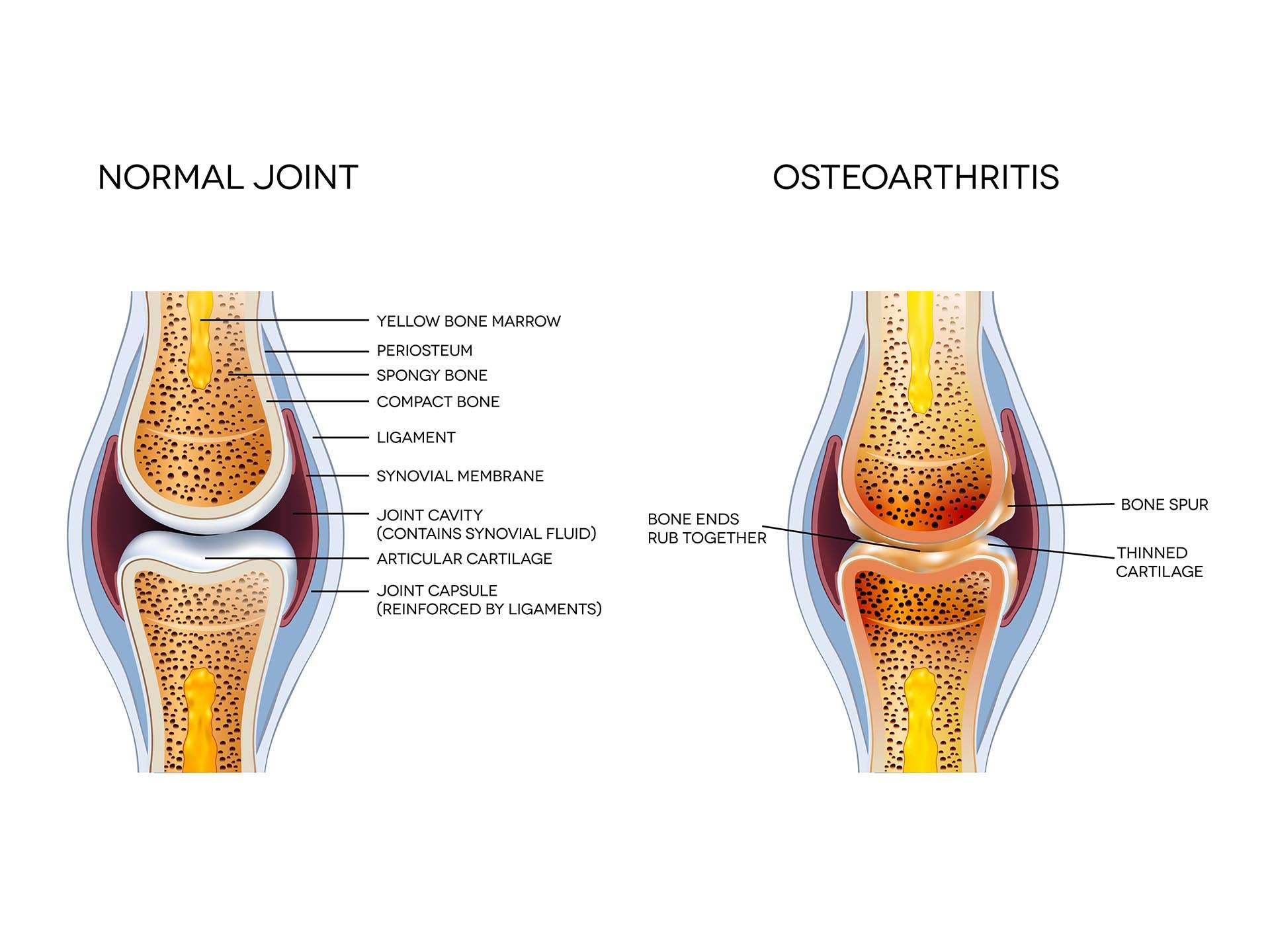
Every form of arthritis is caused due to wear and tear or degeneration of the cartilages over the time .It can be an autoimmune disorder where the immune system of the body itself attacks the tissues and affects the synovium (Covering of the joints) and cartilages. Genetic association a strong familial background and high levels of uric acid in the body also result in arthritis .Arthritis can be of infective in origin, viral or bacterial. It may also be because of certain systemic or metabolic diseases.
Clinical presentation:
Symptoms develop gradually. The most common joints affected are knee, wrist and small joints of fingers. Irrespective of the type of arthritis, pain in joint, swelling and stiffness are the prominent features. Pain may vary from person to person. It can be mild or severe. Difficulty in movement like walking, standing, sitting is experienced by the patient. Formations of nodes on small joints are seen. In cases of infective arthritis sudden onset of chills, fever along with body and joint pain can be seen. Muscle weakness, malaise and tenderness are also present. Gradually over a period of time non responsive or untreated patients develop deformities. Arthritis can be very debilitating.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done of the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the physical examination carried out by the doctor. Certain investigations which can be done are X-ray, MRI or CT scan of the affected joint. Routine blood test and a profile of specialized blood test are done to categories the type of arthritis.
Treatment:
Change in lifestyles is necessary to correct the pain. Weight reduction in obese, adequate rest, correction of wrong postures and regular exercises needs to be adopted. Wearing of braces and supports to hold the joint in alignment during movement, cold and hot compressions along with medications can be advised. Non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAID), steroids, DMARDS (Diseases modifying anti rheumatic drugs) and pain relieving drugs are prescribed. In severe cases corticosteroid injections and topical pain relieving gels and lubricants are advised. Patients who are not responding to medications and with underlying causes as degeneration of the knee joint etc are treated with surgical intervention.
Other Modes of treatment:
Certain other modes of treatment can also be helpful in coping up the symptom. Taking into consideration the symptoms in holistic way, homoeopathy can offer a good aid for the relief of the symptoms. The Ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbs and synthetic derivates can also be beneficial in combating the complaints. Acupuncture which is the science of insertion of fine needles on the certain stimulating spots on the body has proved to be effective. Certain yoga exercises can also be helpful in relieving the pain and strengthening the muscles.
Recent updates:
New studies with electromagnetic therapy are been tested for the efficacy in reduction of arthritic pain.
Scientists at the University of Bristol report some success with stem cell therapy for the treatment of osteoarthritis damage in knees.