Causes and risk factors
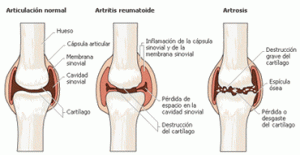
Arthrosis is one of the commonest diseases and is a frequent cause for work absenteeism. Both males and females are equally affected. Arthrosis affects people beginning at the age of 40. Arthrosis is caused by fibrosis or degeneration of the articular cartilage affecting one or various articulations. Typical for arthrosis is destruction of the joints’ cartilage, changes in cartilage and skeletal structures near the joints and a new formation of bone tissue in and around the arthritic joint. The causes are previous trauma, inflammations, infections, advanced age, and genetic predisposition. Being overweight, inappropriate use of the articulation can also lead to arthrosis. The most affected joints are knees, hips, spine, fingers, and toes.
Clinical presentation
Patient presents with pain at the affected site. Pain is usually worse at the end of the day. Joint swelling and warmth is felt at the affected site. Stiffness occurs after long periods of idleness. Pain even at rest is seen in severe cases.
Investigation
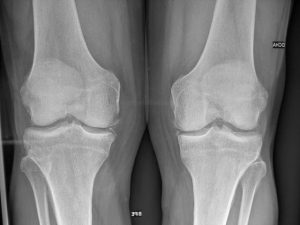
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. X-rays may confirm the diagnosis. The typical changes seen on x-ray include joint space narrowing, subchondral sclerosis, subchondral cyst formation, osteophytes. Routine hemogram is advised. Serum uric acid levels may be advised.
Treatment
There is no treatment to arrest cartilage damage and joint degeneration. Treatment for arthrosis is symptomatic and aims at prevention of further damage and medical complications. Treatment includes lifestyle modification such as weight loss for overweight people. Physical measures like moderate exercise is beneficial to reduce pain and swelling in case of knee and hip arthrosis. Medications such as analgesics, NSAIDs may be required. If disability is severe and the conservative measures fail, joint replacement surgery is recommended.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating arthrosis. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the Ayurvedic system of medicine, which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates, is also found to be effective in treating arthrosis.
Image 1 Image 2