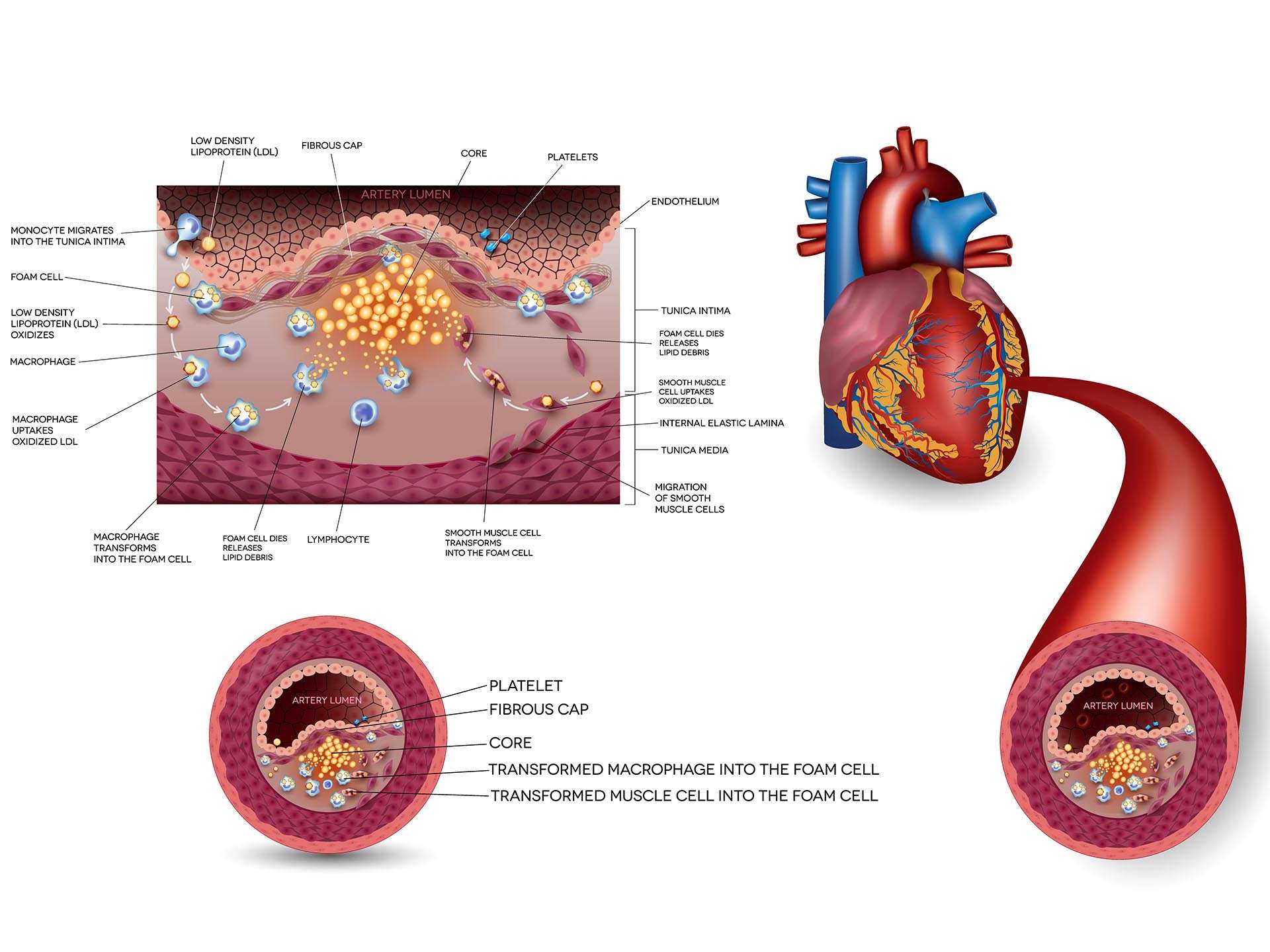
Causative & risk factors
The inner lining of the artery wall is known as endothelium. Any condition that damages the endothelium can lead to clumping of macrophages, LDL (bad) cholesterol on the arterial wall causing atherosclerosis. Common causes are hypertension (high blood pressure), hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hyperlipidemia. Smokers are at a high risk of developing atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is also found to be hereditary in many cases. Those exposed to air pollution are also at a higher risk. Atherosclerosis usually occurs in middle-aged and older individuals and is more commonly seen in males.
The plaques of atherosclerosis sometimes break open, which leads to accumulation of platelets at the affected site. Eventually blood clots are formed giving rise to stroke, heart disease and several other complications.
Clinical presentation
The symptoms of atherosclerosis will be determined by which arteries have been affected.
Affection of the coronary arteries (supply the heart) can cause cardiovascular diseases like angina or heart attacks. The typical symptoms like chest pain, anxiety, vomiting etc. are seen.
Affection of the peripheral arteries (usually the ones supplying the legs) produces symptoms of peripheral arterial disease such as weakness and numbness of the legs, loss of hair, change in skin color etc.
Affection of the carotid arteries (supply the brain) can cause a stroke. The typical symptoms like weakness, numbness, paralysis, headache etc. are produced.
Affection of the renal arteries (supply the kidneys) can give rise to symptoms of chronic kidney disease.
Investigations
Complete medical history of the patient will be able to determine whether he/she is at risk of developing atherosclerosis.
Blood tests will be carried out to test lipid profile, blood sugar levels, thyroid hormone levels etc.
A non-invasive CT angiogram can be performed to view the changes in the arteries.
An invasive procedure called angiography can be performed to visualize the arteries, their circulation and blockages present.
Treatment
Making lifestyle changes is an important aspect of treating atherosclerosis and preventing complications.
The patient is advised to eat healthy, exercise regularly and maintain a balanced body weight.
Medications are prescribed to lower the blood cholesterol levels, to reduce the blood pressure, to prevent blood clotting and hypoglycemic drugs in case of diabetics.
Severe cases of atherosclerosis are treated with a surgical procedure called angioplasty. In this the blockage is removed and the affected artery is expanded so that the blood within can start flowing normally again.
Some patients may be required to undergo CABG (coronary artery bypass grafting).
Statistics
Atherosclerosis and the complications it produces are attributed to be the single biggest cause of death in the developed countries.