Causes and risk factors
Athetosis occurs due to degeneration of the basal ganglia. It can be caused by asphyxia, neonatal jaundice, Huntington’s disease, stroke, trauma, encephalitis, and other CNS infections, or cerebral palsy. It can also be drug induced.
Clinical presentation
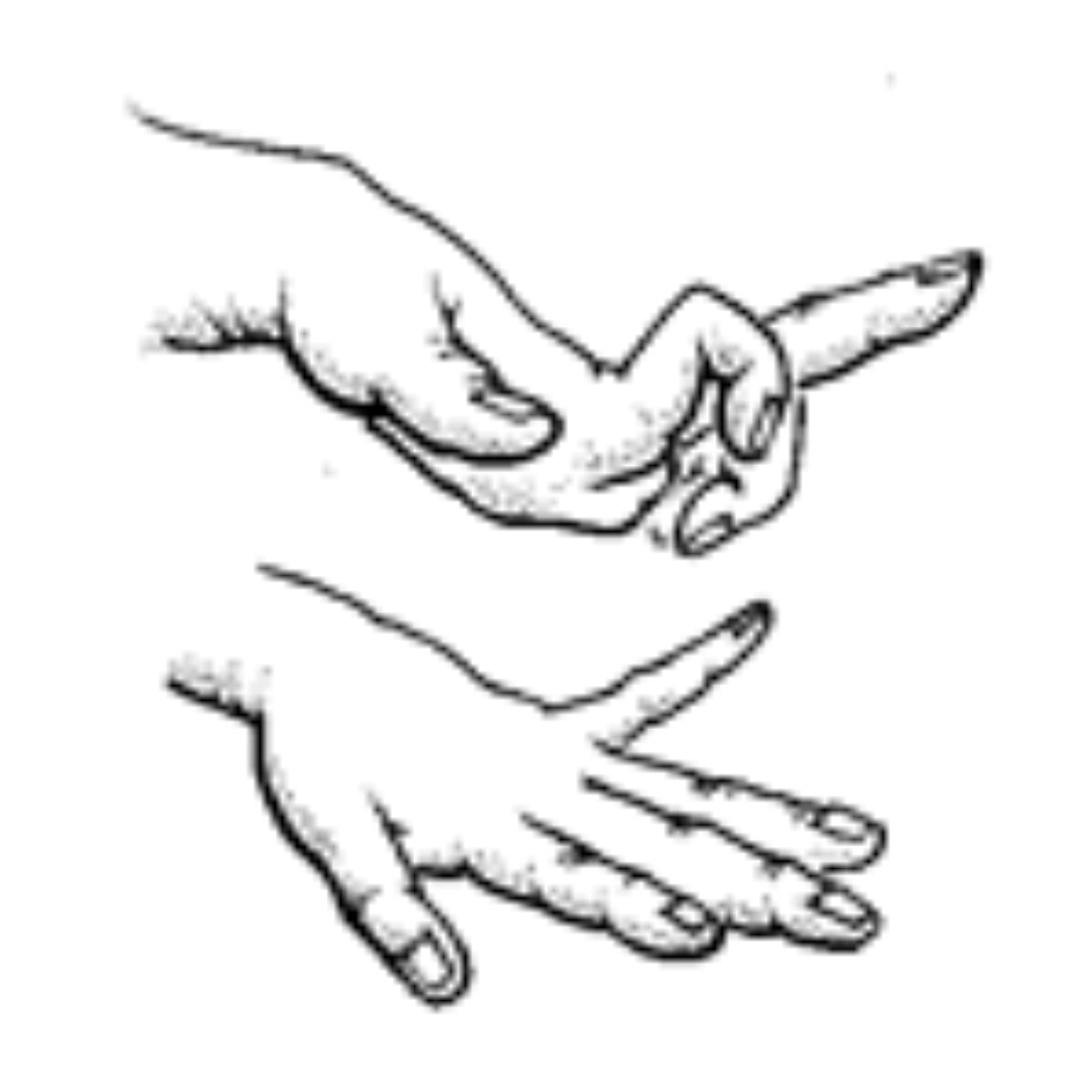
Athetosis commonly affects hands and feet. Patient presents with unbalanced, involuntary movements of muscles, difficulty in maintaining a symmetrical posture; writhing, convoluted movement of the digits. They occur on holding the parts of limbs in certain specific position or posture.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. CT scan or MRI of the head or affected area is recommended. EEG is required. Lumbar puncture is advised. Urinalysis, CBC is done. Electromyography and nerve conduction velocity studies are done.
Treatment
Medical treatment involves antipsychotic drugs that block dopamine action. Certain surgical procedures may be applied, such as subthalamotomy, i.e., removal of a part of the cerebral motor cortex, cutting a part of the posterior spinal roots. Training the patient to re-learn the movements also contributes to the treatment.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating athetosis. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the Ayurvedic system of medicine, which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates, is also found to be effective in treating athetosis.