Causes and risk factors
Band keratopathy can be caused due to a variety of local and systemic causes. Normally various body fluids like tear, serum, aqueous fluids, etc., contain calcium. Evaporation of tears can cause the fluids to become concentrated. This leads to deposition of calcium on the cornea. Increased level of calcium and phosphate in serum along with alteration in the pH of the corneal surface is another contributing factor. End-stage glaucoma, anterior mosaic dystrophy along with chronic uveitis is the major eye diseases which increase the risk for band keratopathy. Various systemic diseases renal failure, Paget’s diseases, high intake of vitamin D along with hyperparathyroidism contribute to the same. Band keratopathy can also occur as a side effect of certain medications or chemicals.
Clinical presentation:
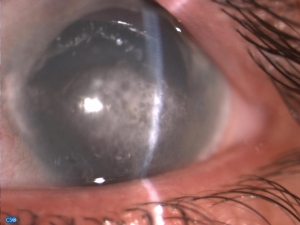
The complaints can affect either one eye or both the eyes. Deposition of calcium usually starts at the center and then spreads to the periphery; however, vice versa can also occur. Thick plaque like layer is seen on the cornea. The patient can also complain of pain in the eyes, continuous watering of eyes, and decrease vision. There is a sensation as if some foreign body has been logged inside the eyes. The eyes become typically red and vision becomes blurred.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done of the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the examination carried out by the ophthalmologist. Penlight lamp and slit lamp instruments are used for examining the eyes. Corneal cultures, and in certain severe cases, biopsy is needed. Certain other investigations like routine blood test, serum test for calcium and phosphates, urine routine, blood sugar levels, etc., can also be advised.
Treatment:
There is yet no effective treatment available for this condition. Treating the underlying cause is the main line of treatment. Medications to reduce the level of calcium and phosphate are advised. Superficial debridement of the cornea is an effective treatment in most of the cases; however, it does have certain adverse effects.
Complications:
Band keratopathy can lead to corneal scarring, ulceration, or even blindness.
When to contact a doctor:
If the patient suffers from any complaints of redness of eyes along with blurred vision, one should consult an ophthalmologist.
Prevention:
Regulation on dietary intake of calcium and vitamin D is the essential preventive measure to be adopted.
System involved: Ophthalmic system.
Organ involved: Eyes, cornea.