Causes and risk factors
There is no clear explanation regarding what causes dysmorphophobia. Biological, psychological, and even social or cultural factors are thought to contribute. Seen more commonly in female gender. A history of depression, anxiety, or psychosis may be present.
Clinical presentation
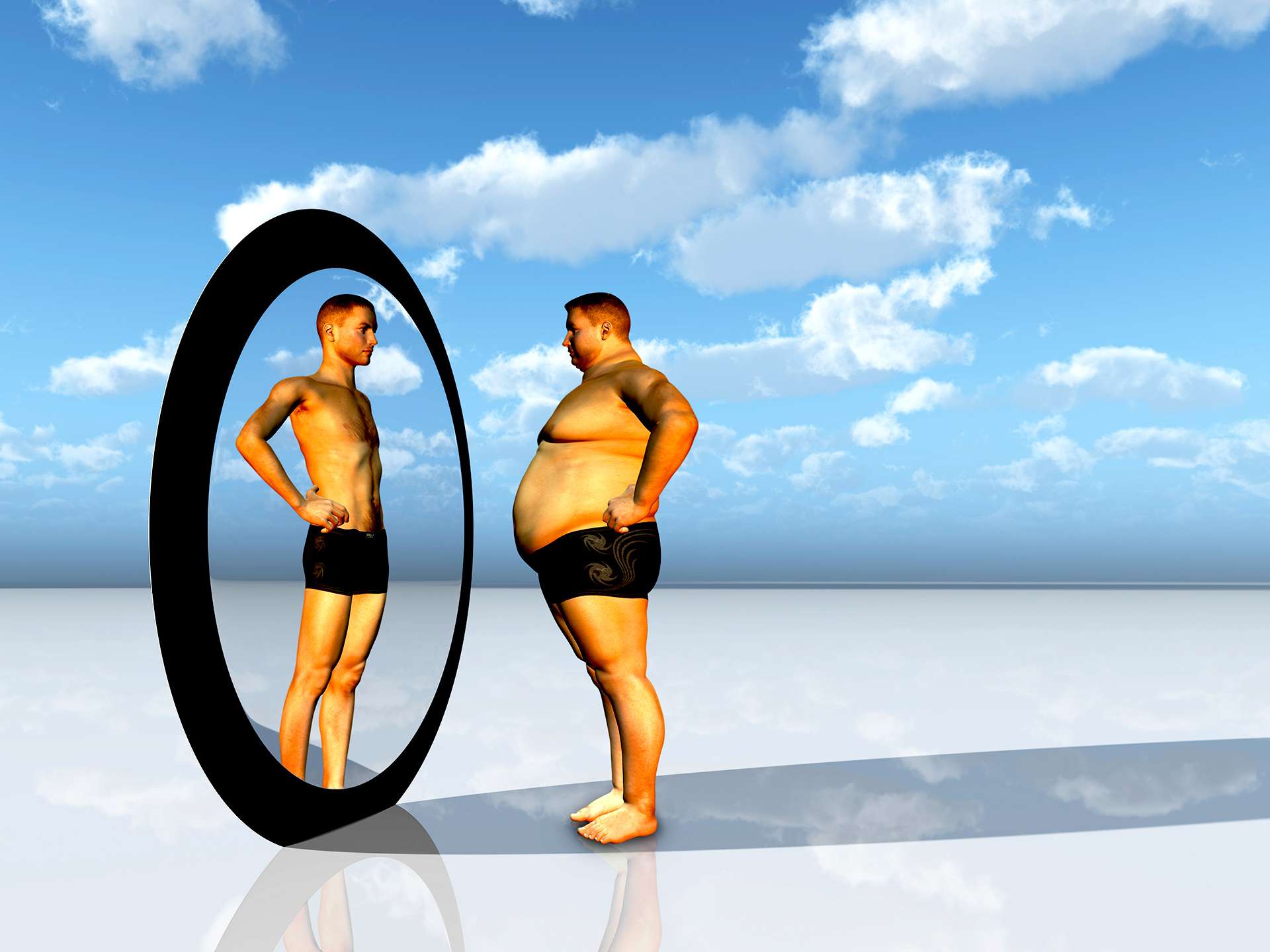
Symptoms of dysmorphophobia include obsessed with a perceived physical flaw which may be minor, or even imagined, frequently checking oneself into mirror or other reflecting surfaces, comparing oneself with others, may describe oneself as unattractive or deformed or even looking like a monster, camouflaging a part with clothing, makeup, hat, hair, or hand, frequently touching the supposed defect, restricted diet, excessive grooming, avoiding having photos taken. The symptoms are often associated with fears of rejection and feelings of low self-esteem, shame, embarrassment, unworthiness, and being unlovable. Patient has a feeling of self conscious and anxiety going out in public, facing problems at school, work or in relationships; frequently visiting doctors, skin specialist to get rid of the affected part. Most common areas of concern for a patient with BDD are wrinkles, scars, acne, body hair – scarce or plenty, facial features often involving nose, body weight. Other areas include penis, breasts, buttocks, thighs, body odours.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and psychological evaluation by the psychiatrist or psychotherapist helps in diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment involves psychotherapy and counselling which involves cognitive and behavioural therapy, relaxation techniques to combat the problem. Increased social involvement, spending quality time with family, social interactions will also help in managing the condition. Medications such as antidepressants, anti anxiety or antipsychotic drugs may be required.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating BDD. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating BDD.