Causes and risk factors:
Bronchitis can develop after any acute viral infection. The major causative organisms are influenza, rhinovirus, adenoviruses, or parainfluenza virus.Infection by cbacterias like streptococcal and staphylococcal can also lead to bronchitis. Smoking ,Atmospheric pollution, recurrent respiratory infection in childhood are the contributing factors. Low birth weight babies and people engaged in occupation like coal miner, and industrial worker are more prone for suffering from bronchitis
Clinical presentations:
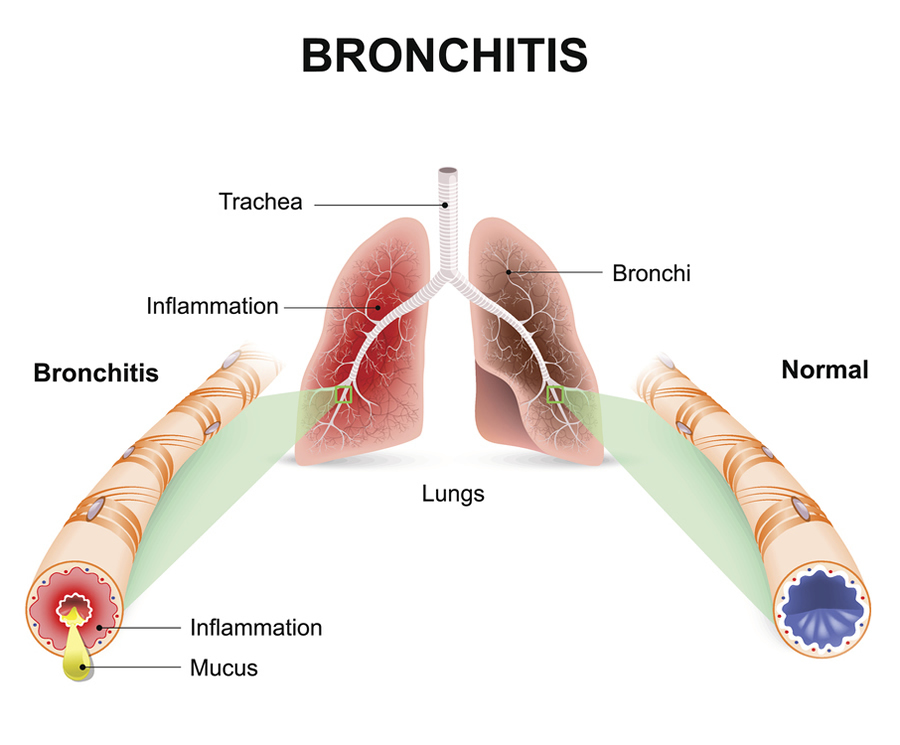
Cough with expectoration is the cardinal symptom of bronchitis. The sputum expelled out is mucoid or mucupurelent. The cough is aggravated due to exposure to cold or during winter but later it becomes continuous. Long standing cough an cause shortness of breath. A whistling sound is produced during breathing. A sound somewhat like snoring can also be heard on examination of the chest by the doctor. These patients tend to put on weight and there occurs bluish discoloration of the mucus membrane and nails (Cyanosis) Acute respiratory infective attacks can lead to fever and can aggravate the complaint of cough.Sorethroat, malaise, Coryza can be the other complaints associated with cough. Long standing cough can lead to complications like emphysema, fibrosis of lung, right heart failure or hernia at various sites. People who do not smoke are exposed to the chronic smoker (Passive smoking) are predisposed to bronchitis.
Diagnosis and investigations:
Symptoms narrated by the patient and the physical examination carried out by the doctor will help to confirm the diagnosis. Certain investigations can be advised which are routine blood test, chest X ray and culture of sputum is done to find out the causative agent. Along with this pulmonary function test is a useful aid for diagnosis, Measurement of arterial blood gas and ECG can be done to rule out other causes related to heart.
Treatment:
Complete abstinence from smoking is the most important measure, steam inhalation and use of hot drinks can provide temporary relief. Use of protective mask to avoid the adverse effect of pollution can be done. Bronchodilating medications are prescribed. In cases with infection antibiotics can be given. Use of meter dose inhalers (MDI), nebulisation and use of humidifiers is recommended.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating sciatic pain. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating pain. Yoga exercises and pranayam are really found to be effective.