Causative & risk factors
It is believed that body’s immune system instead of producing antibodies against invading bacteria and virus produces antibodies which affect healthy skin.
Some cases may be triggered by certain medications, ultraviolet light therapy and radiation treatment.
Clinical presentation
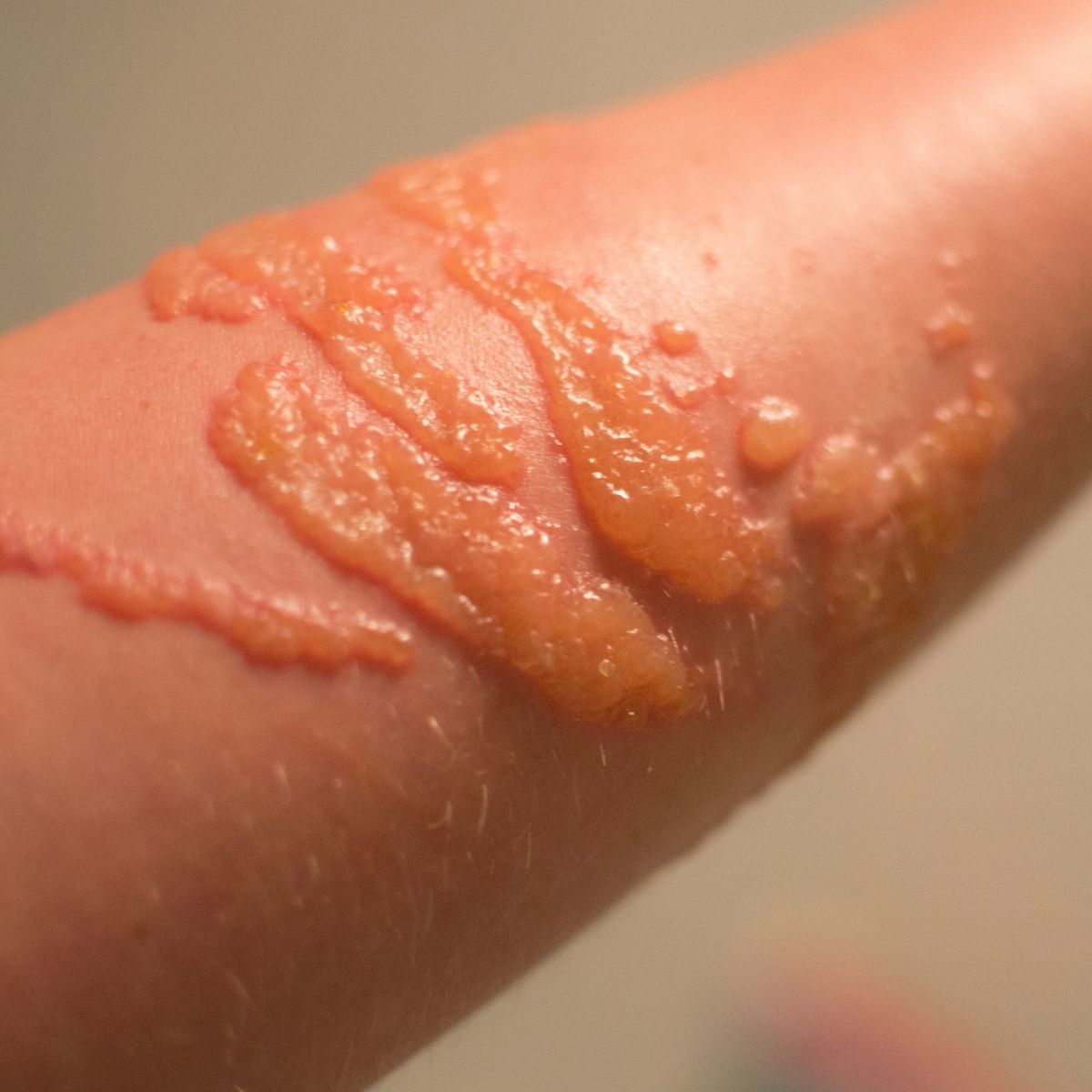
Bullous pemphigoid is characterized by the appearance of large fluid filled blisters on the skin. The blisters contain clear fluid and sometimes blood. Common locations are the groin, upper thigh area, lower portion of the abdomen and the arms. Pruritus (itching) may be present in the affected skin areas. Blister may be preceded by urticaria in some cases.
Complications of bullous pemphigoid include secondary infection and sepsis.
The outcome is variable with periods of aggravation and amelioration. It is poor in elderly people with poor health. Untreated cases can be fatal.
Investigations
Diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid is based upon your symptoms and the result of the biopsy of the affected skin.
Treatment
Topical or systemic steroids are prescribed in severe cases. Immune suppressing medicines are given to reduce hyperactivity of the immune system. Antibiotics are prescribed for people who cannot tolerate steroids.