Causes and risk factors
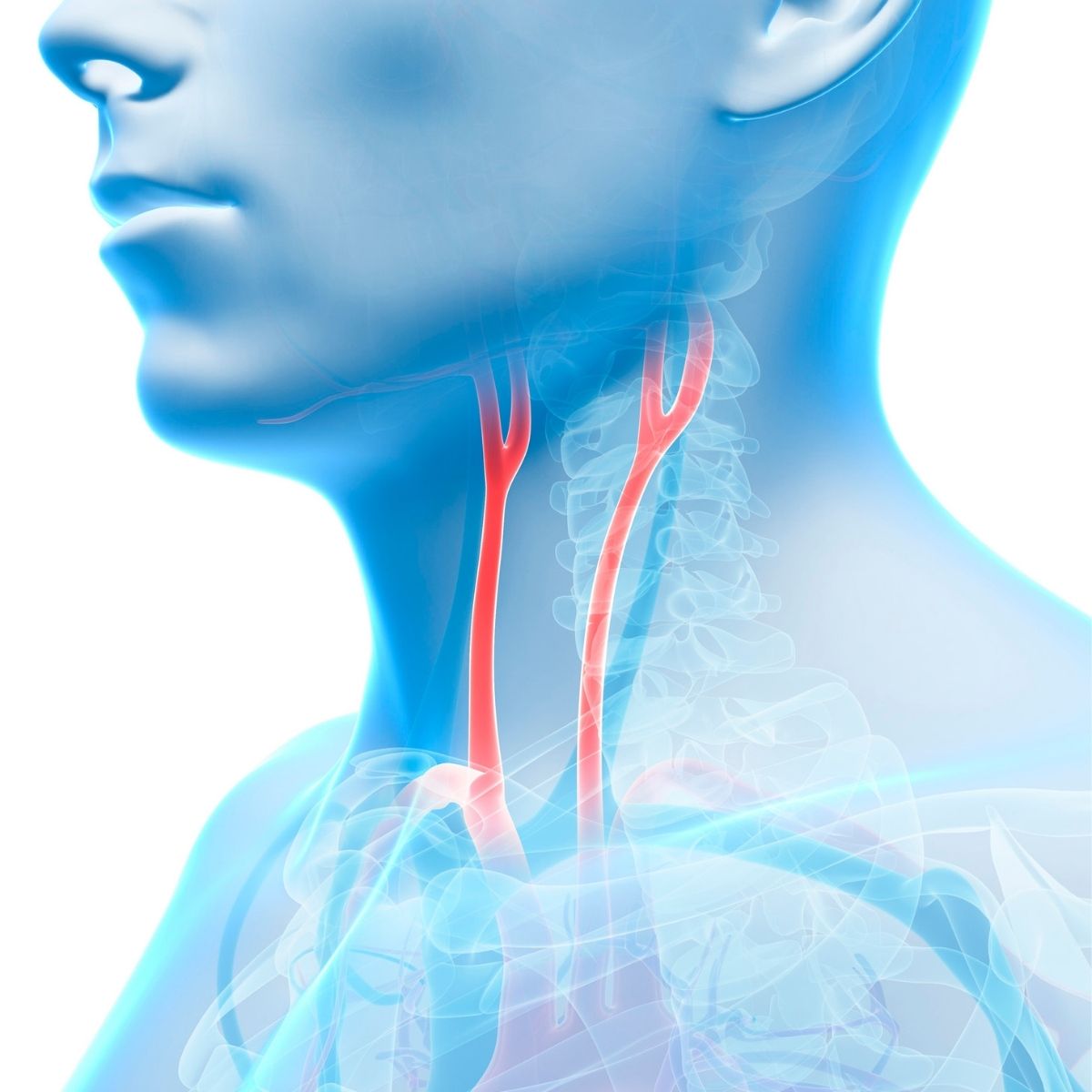
Carotid artery disease occurs when sticky, fatty substances called plaque builds up in the inner lining of the arteries. The plaque may slowly block or narrow the carotid artery hampering the blood flow through the artery or cause a clot [thrombus] to form. Risk factors for blockage or narrowing of the arteries include high blood pressure, diabetes, heart diseases, high levels of low density lipoprotein, kidney disease, especially when dialysis is needed. Smoking, heavy alcohol use, cocaine abuse leads to the disease. Family history of atherosclerosis, stroke, increasing age is the predisposing factors for carotid artery disease. Two uncommon conditions called Marfan syndrome and fibromuscular dysplasia [abnormal growth or development of the cells in the walls of carotid arteries] may also cause narrowing of the carotid arteries.
Clinical presentation
Carotid artery disease does not produce any signs and symptoms in early stage. When the blockage is severe enough to reduce blood supply to your brain signs of transient ischemic attack [TIA] or stroke are seen. TIA is an alarming sign for future possibility of stroke. Signs and symptoms include numbness or tingling on one side of the body, weakness on one side of the body, lack of coordination and balance, clumsiness, or trouble in walking is seen. He has difficulty swallowing, difficulty writing or reading. Drooping of the face is observed. Lack of control over the bladder or bowels is seen. Patient is unable to recognize objects or people, there is confusion or loss of memory, trouble saying or understanding words, change in alertness. Changes in feeling, including touch, pain, temperature, pressure, hearing, and taste. Loss of vision in one or both eyes is experienced. There can be personality, mood, or emotional changes.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. During physical examination the physician may hear an abnormal sound called as bruit when using a stethoscope to listen to the blood flow in your neck. The following tests are done -Carotid duplex or Doppler study to see how well blood is flowing through the carotid artery, Magnetic resonance angiography [MRA], Computerized tomographic angiography [CTA]. Carotid or cerebral angiographies are recommended.
Treatment
Treatment options include lifestyle modifications like following a healthy diet plan, maintaining healthy weight, keeping blood pressure and blood cholesterol levels under check, quitting smoking, moderate consumption of alcohol. Medications like Anti-platelet medications to prevent formation of blood clots, Anti cholesterol medications to lower cholesterol levels are required. Surgical procedures include Carotid endarterectomy, Carotid angioplasty and stenting.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating carotid artery disease. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating carotid artery disease.