Causes and risk factors
The exact cause of cancer is not known, but various risk factors or predisposing factors have been put forth. It is found that the cells undergo an uncontrolled and abnormal proliferation which gives rise to formation of tumors. Genetic predisposition is one of the major causes. Certain infections predisposes cervical cancers, human papillomavirus is the common among it. Among those, infection due to HPV strain 16 and 18 are more commonly seen. This viral infection spreads during sexual intercourse. Immuncompromised females are also at high risk of developing cervical cancers. Cervical cancers can be due to metastasis of malignant condition present elsewhere in the body.
Clinical presentation
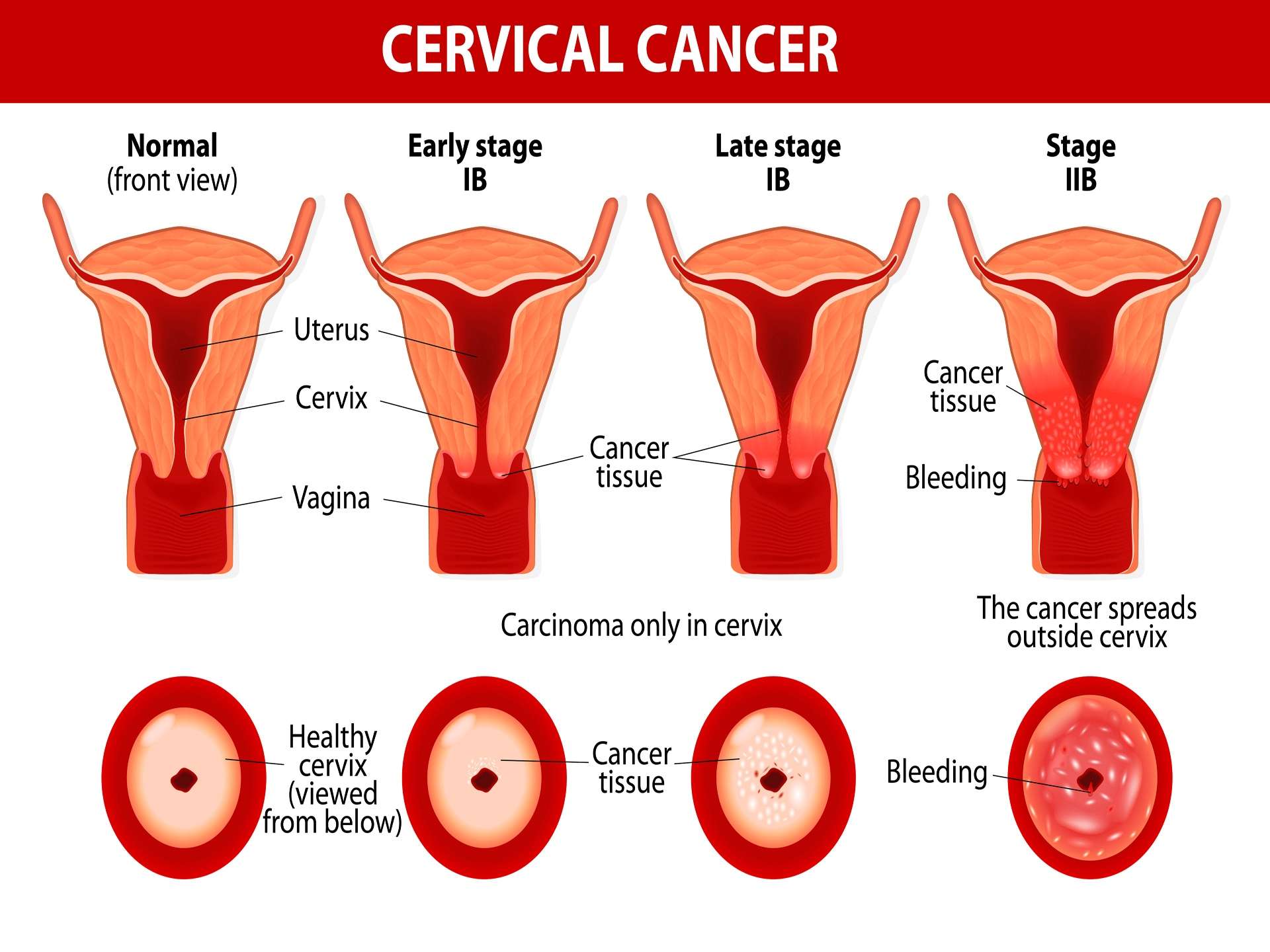
There are different types of cervical cancer-Squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, small cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma and glassy cell carcinoma.
In the early stages of formation of a tumor no signs and symptoms are evident.
As the tumor increases in size, following symptoms can be seen vaginal bleeding other than menstruation is seen. Irregularities in menses occur. The bleeding is either profuse or prolong. Dull aching pain and discomfort in the pelvic region is felt. The pain may radiate to the back. The patient can come with complaints of pain during intercourse. Abnormal vaginal discharges can also be seen. Fatigue, loss of appetite and weight loss are other associated symptoms seen.
Investigations
Diagnosis is done of the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the recto vaginal examination carried out by the gynecologist. Hysteroscopy for internal visualization of the uterus and Pap smear are done. Biopsy is the diagnostic investigation. Trans vaginal or abdominal sonography, Cystoscopy, proctoscopy, CT scan can be done. In addition to these Routine blood, CA 125 blood test, ultrasonography, and MRI scans are advised for metastasis.
Treatment
Depending upon the extend and stages of cancer the treatment is planned. Various surgical approaches can be adopted. Conization and Trachelectomy are some of the surgical methods which can be adopted. Hysterectomy is found to be effective in cases where metastasis has not occurred. Radiation therapy is used. Targeted chemotherapy and immunotherapy agents are administered. Along with the above-mentioned treatment, certain preventive measures need to be implemented. All sexually active women should get vaccinated against Human papilloma virus Use barrier contraceptive devices during sexual intercourse. E.g.: condoms. Use barriers for oral sex. E.g.: dental dams
Regular pap smears should be done. In women between the age of 21-29, it should be done after every 2 years and in women after the age of 30, it should be done after every 3 years.
Recent update:
As per the American cancer society, many new techniques for better treatment have been researched.