Causative and risk factors
Chicken pox is caused by the varicella zoster virus which is highly contagious. It is spread through the following means:
- airborne particles
- droplets in exhaled air
- fluid from the blisters or sores
- by contact with articles of clothing
Patients are contagious a few days prior to the appearance of rashes as well as a few days later. So it is possible to catch the infection from someone without any visible symptoms of chicken pox.
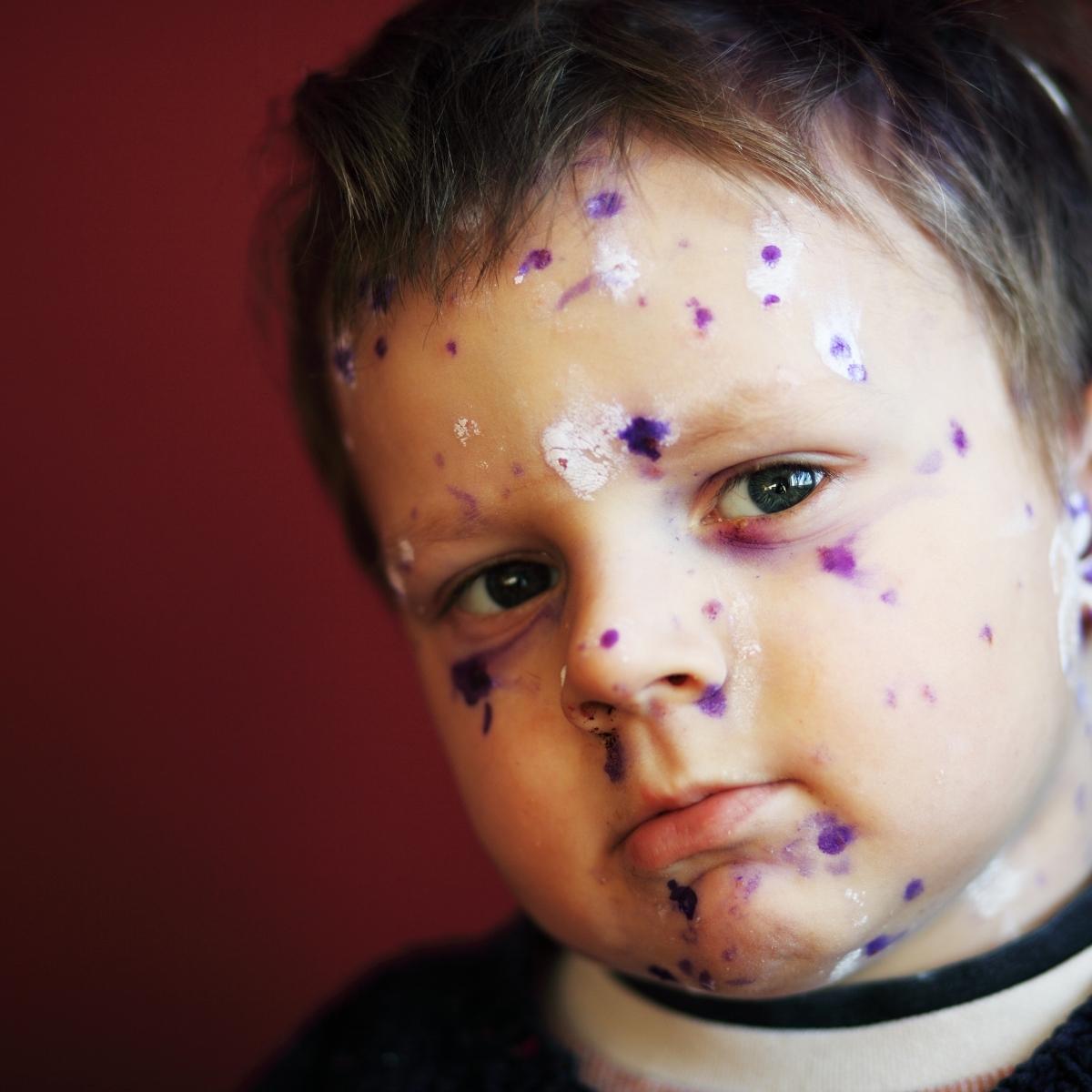
Clinical presentation
The initial symptoms of chicken pox include high fever, headache and malaise. There is pain in the stomach and a lack of appetite.
Later, typical chicken pox rash develops which consists of crops of red papules initially on the scalp. They then spread to the trunk and limbs. These papules then form blisters and open sores. These eruptions then crust and form scabs and eventually heal completely.
In most cases, chickenpox runs its course and disappears in about 2 weeks. The outcome is better in children than in adults. However, the virus remains latent in the human body and may give rise to herpes zoster eventually.
Chicken pox may give rise to complications like scarring and secondary bacterial infection of the lesions. It can also lead to infection or inflammation of the brain (encephalitis, cerebellar ataxia). Other complications include Reye’s syndrome, nerve palsies, pneumonia and death in some cases.
Diagnosis & Investigations
Chicken pox is generally diagnosed on the basis of physical examination and medical history alone. Occasionally, the lesions may undergo a culture testing.
Treatment
Chicken pox usually heals on its own after running its course for a few days and only supportive care is essential. Anti-pyretic medications are prescribed for fever and antihistaminic medications for itching. Antiviral drugs may be prescribed in some cases. Oatmeal baths, calamine lotion etc can be used for relief.
Undergoing vaccination for chicken pox is the best way to prevent it. The varicella vaccine is extremely effective in preventing this infection. Even when infected, the vaccinated person will develop a much milder illness than unvaccinated people. Most countries recommend chicken pox vaccine to all children in their national vaccination programs.
Recent updates
A study suggests that children who catch chicken pox have a 4 times higher stroke risk in the 6 month period after the infection.