Causes and risk factors
The exact cause of dermatitis is not known. There are different varieties of dermatitis, but the common among them are contact dermatitis (irritatant dermatitis and allergic), atopic and seborrheic.
It results from a combination of several factors. A number of genes i.e. genetic factor is responsible for developing dermatitis. A person suffering from asthma and other allergies are more prone for development of dermatitis. Certain individual are sensitive to some types of chemicals. Use of certain cosmetics perfumes, hair dyes, use of certain chemicals in industries, use of latex gloves can also lead to dermatitis. Irritant dermatitis is due to contact with the irritant material and allergic dermatitis is an hypersensitivity reaction to the allergic substance. People with oily skin are susceptible for developing seborrheic type. Infections harbors in such types of skin. In infant’s persistent contact with moist napkin, frequent changing of napkins leads to damage of the skin.Atopic dermatitis is common in infants and children in flexor parts of joint like elbow, behind the knees and neck region. Dermatitis can also be seen secondary to certain other skin conditions like scabies, HIV, diabetes mellitus or Candida infection.
Clinical presentation:
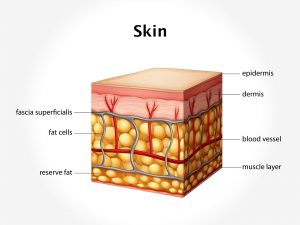
The common sites of affection are scalp, neck, flexor aspect of knees and elbows and buttocks or perianal region. The patient presents with complaints of redness of the affected area. Itching and small eruptions are the characteristic features seen. The eruptions are small skin lesion filled with fluid. Severe itching can lead to oozing of the blood. On the contrary itching itself can aggravate the complaint and give way for secondary infections. White flakes on scalp (dandruff) are seen.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done on the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the physical examination carried out by the doctor. Patch test is diagnostic test. Routine blood test, allergic test and certain specialized blood test for diagnosing the underlying cause can also be suggested.
Treatment:
The dermatologist can recommend certain anti fungal creams along with corticosteroid ointment. Use of calamine lotions (Not for prolong use in dry skin) is advised. Medications may vary as per the underlying cause of itch. Light therapy is an effective measure seen. Maintaining of good skin care needs to be implemented. Use of appropriate skin moisturizer is suggested specially for dry skin. Bland soothing moisturizers are recommended. Exposure to certain chemical and soaps should be avoided. In cases of sensitivity to certain substances protective gloves or use of barrier cream is advised. Compresses are helpful in wet eczemas. Adequate hydration and balanced nutrition intake is necessary.
Other modes of treatment:
Certain other modes of treatment can also be helpful in coping up the symptom. Taking into consideration the symptoms in holistic way, homoeopathy can offer a good aid for the relief of the symptoms.
Recent updates:
As per the article published in medindia a study found that daily treatment with a vitamin D supplement significantly reduced the symptoms of winter-related atopic dermatitis.
Researchers have found that nickel and chromium found in mobile phones are sufficient to induce allergic contact dermatitis.