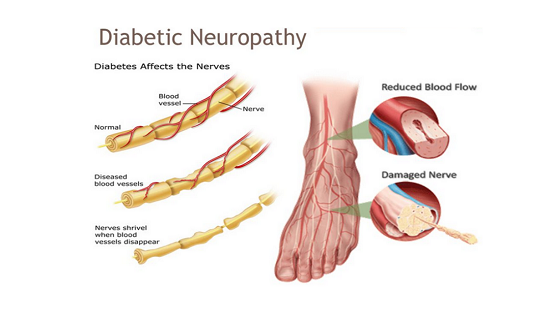
Causes and risk factors
Uncontrolled diabetes is main cause of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes consists of high blood sugar levels. High blood glucose interferes with the ability of the nerves to transmit signals. It also weakens the capillary walls that supply the nerves with oxygen and nutrients. Other factors that contribute to diabetic neuropathy include inflammation in the nerves caused by an autoimmune response. Smoking or alcohol abuse aggravate the condition.
Clinical presentation
There are four types of diabetic neuropathy: peripheral, autonomic, proximal, and focal. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy refers to damage to peripheral nerves, especially of the feet and legs. Diabetic proximal neuropathy affects nerves in the thighs, hips, or buttocks. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy affects the autonomic nervous system; the gastrointestinal, urinary, genital, or vascular systems. Diabetic focal neuropathy affects a specific nerve or area at any site in the body. Symptoms of Diabetic neuropathy include numbness and tingling of extremities, burning or electric pain. Dysesthesia [abnormal sensation to a body part], facial, mouth and eyelid drooping, vision changes, muscle weakness, difficulty swallowing, speech impairment, fasciculation [muscle contractions] and dizziness are experienced. Diabetic autonomous neuropathy can affect blood vessels to sex organs, urinary system, gastrointestinal tract leading to symptoms like erectile dysfunction in men, anorgasmia, retrograde ejaculation [in males], urinary incontinence, diarrhoea, constipation respectively.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Blood sugar levels are checked at first. The following tests may be performed such as Filament test in which sensitivity to touch may be tested using a soft nylon fibre called a monofilament. Nerve conduction studies, Electromyography [EMG], Quantitative sensory testing is recommended.
Treatment
Diabetic neuropathy has no known cure. Treatment for diabetic neuropathy focuses on relieving the symptoms and slowing the progression of the disease. Strict control of blood sugar levels is required. Analgesics are necessary to relieve pain.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating Diabetic neuropathy. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating Diabetic neuropathy.