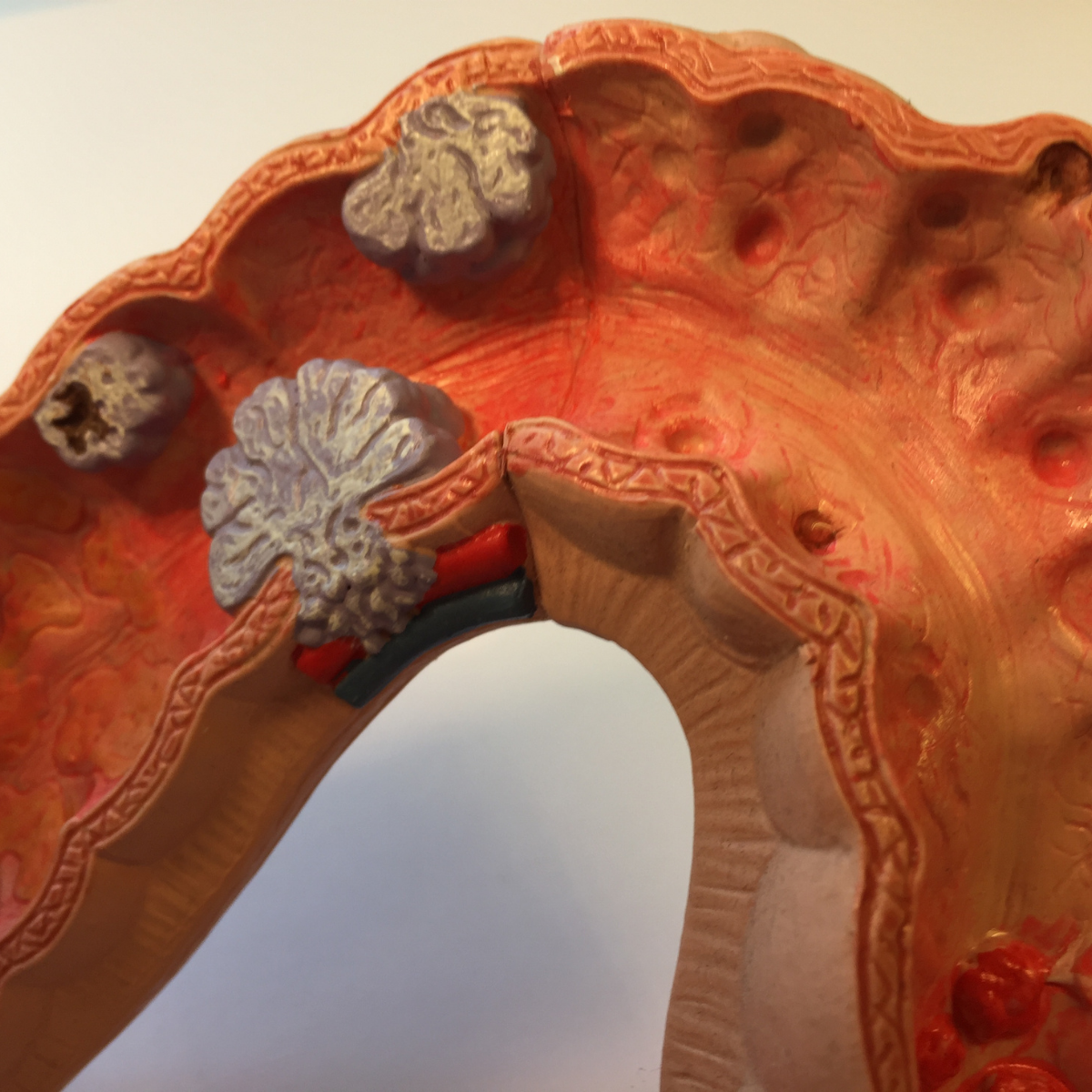
Causative and risk factors
The cause of diverticulitis is unknown. The risk factors identified for the formation of diverticulitis are advancing age, inactivity and obesity. Frequent intake of painkillers, smoking and a fat-rich diet are also known risk factors of diverticulitis.
Diverticulitis can give rise to complications like formation of a diverticular abscess or fistula or peritonitis.
Clinical presentation
Diverticulitis presents with severe abdominal pain and tenderness, especially in the lower left area. The abdomen is usually found to be distended. The patient has a reduced appetite, nausea or vomiting, fever and weakness. Constipation or profuse watery diarrhea may be present along with bleeding per rectum.
Diagnosis & Investigations
Your doctor will first carry out a physical exam to locate the site of pain in the abdomen. Diverticulitis must be differentiated from other causes of abdominal pain such as gastroenteritis, pancreatitis, appendicitis etc.
A complete blood count of the patient reveals elevated WBC with marked predominance of polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Imaging tests such as a plain X-ray of the abdomen or barium enema are performed. CT scan of the abdomen may be done to visualize the diverticuli properly. Sigmoidoscopy is done to visualize the diverticuli from within through an endoscope.
Treatment
A high fiber diet is advised to patients with diverticulosis in general. However, during acute attacks of diverticultis, a liquid diet is advocated.
Admission to hospital becomes necessary in severe cases. Antibiotics can be given orally or intravenously. Drugs to relieve pain are prescribed. Parenteral nutrition is recommended in severe cases to keep the gastro-intestinal tract empty. Nasogastric suction may be necessary to empty the stomach contents
Role of surgery – Multiple episodes of diverticulitis or presence of complications may necessitate surgery in some patients.
Resection of the bowel: The diseased portion of your bowel is removed and the healthy portions are joined together.
Colostomy – If your bowel is damaged excessively, then a colostomy may be needed. In this procedure, an opening is made in the abdominal wall so that products of excretion can pass from a healthy portion of the bowel directly into a connecting bag outside the body. Later, this colostomy may be reversed once the bowel becomes functional again.