Causes and risk factors
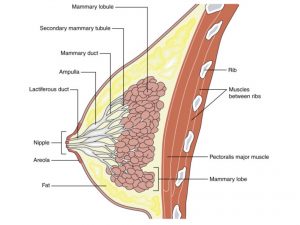
The exact cause of DCIS is unknown. It is found to be caused due to genetic mutations in the DNA of ductal cells of the breast. It can be inherited. There are some risk factors which are associated with the disease like age above 50 years, women who have height more than average, overweight women, close relatives with breast cancer, past history of breast cancer, past history of non-cancerous lumps, dense breast tissue, women on hormones replacement therapies, women with early menarche or late menopause, women with first pregnancy after age 30, radiation exposure, alcohol consumption, jobs causing exposure to carcinogens or endocrine disturbance. It is common in females, but can also occur in males.
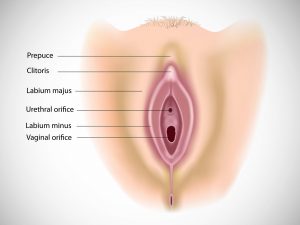
Clinical presentation
A patient with DCIS is mostly asymptomatic. She may experience a small lump in breast. There can be abnormal or bloody discharge from nipple. Slight pain or tenderness in breast may be experienced by some patients. Additional symptoms may include swelling in the armpit, flattening or indentation on the breast, change in the size, contour, texture, or temperature of the breast.
Investigation
Self breast examination may reveal lump in breast. Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Mammogram is an essential diagnostic tool for early detection of any type of breast cancer. Calcifications in the breast tissue seen in mammogram suspect the disease. Further investigations include fine needle aspiration cytology [FNAC] which confirms the diagnosis. Imaging studies such as USG of breast, MRI scan of breast is useful for further evaluation.
Treatment
Treatment depends upon the stage of cancer. Most patients with DCIS are treated with breast conservation treatment such as lumpectomy. It is followed by radiation treatment. Supportive care is given to prevent further spread of cancer such as medicines by chemotherapy, hormonal therapy and targeted cell therapy. In case of DCIS involving multiple ducts, mastectomy is recommended.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating DCIS. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating DCIS.
Facts and figures
Out of total breast cancers 83% are diagnosed as DCIS. 20 to 53 % of women with DCIS develop invasive breast cancer if left untreated.
![Ductal Carcinoma In Situ [DCIS]](https://moho.loopshell.com/read/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Ductal-Carcinoma-In-Situ-Dcis.png)